
A flagship conference of the IEEE Signal Processing Society, GlobalSIP is structured around coherent symposia that explore new and emerging developments in the field, while maintaining a format that encourages accessibility to interested researchers and fosters interaction and cross-pollination of ideas.

- Read more about ROBUST ONLINE MULTI-OBJECT TRACKING BASED ON KCF TRACKERS AND REASSIGNMENT
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views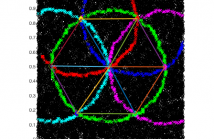
We consider the problem of determining the Euclidean embedding of a dense, planar sensor network. The sensors are equipped with a binary sensing protocol that enables them to detect the neighboring sensors within a fixed radius, R. Using only this connectivity graph, we reconstruct an approximate embedding of the network on an Euclidean plane. To that end, we design an algorithm to identify special landmark nodes in the network whose Euclidean embedding is ``close'' to the vertices of an ideal hexagonal lattice.
- Categories:
 79 Views
79 Views
- Read more about Tracking Time-Vertex Propagation using Dynamic Graph Wavelets
- Log in to post comments
Graph Signal Processing generalizes classical signal processing to signal or data indexed by the vertices of a weighted graph. So far, the research efforts have been focused on static graph signals. However numerous applications involve graph signals evolving in time, such as spreading or propagation of waves on a network. The analysis of this type of data requires a new set of methods that takes into account the time and graph dimensions. We propose a novel class of wavelet frames named Dynamic Graph Wavelets, whose time-vertex evolution follows a dynamic process.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Graph-Based Active Learning: A New Look at Expected Error Minimization
- Log in to post comments
In graph-based active learning, algorithms based on expected error minimization (EEM) have been popular and yield good empirical performance.
The exact computation of EEM optimally balances exploration and exploitation.
In practice, however, EEM-based algorithms employ various approximations due to the computational hardness of exact EEM.
This can result in a lack of either exploration or exploitation, which can negatively impact the effectiveness of active learning.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about LOW-LATENCY SOUND SOURCE SEPARATION USING DEEP NEURAL NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
Sound source separation at low-latency requires that each in- coming frame of audio data be processed at very low de- lay, and outputted as soon as possible. For practical pur- poses involving human listeners, a 20 ms algorithmic delay is the uppermost limit which is comfortable to the listener. In this paper, we propose a low-latency (algorithmic delay ≤ 20 ms) deep neural network (DNN) based source sepa- ration method.
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views
- Read more about A probabilistic interference distribution model encompassing cellular LOS and NLOS mmWave propagation
- Log in to post comments
We propose a novel probabilistic model for the interference power distributions in a cellular network employing MIMO beamforming in mmWave spectrum. Considering both line-of-sight (LOS) and non-line-of-sight (NLOS) propagations, we use the Gamma distribution for LOS interference power, and propose a mixture of the Inverse Gaussian and Inverse Weibull distributions for the NLOS interference power. For the NLOS mixture model, an expectation maximization algorithm is developed using both analytical moment matching and maximum likelihood estimation.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
- Read more about COMMUNITY DETECTION FROM GENOMIC DATASETS ACROSS HUMAN CANCERS
- Log in to post comments
Cancers originating from different organs can show similar genomic alterations whereas cancers originating from the same organ can vary across patients. Therefore cancer stratification that does not depend on the tissue of the origin can play an important role to better understand cancers having similar genomic patterns irrespective of their origins. In this work, we formulated the problem as a weighted graph and communities were found using a modularity maximization based graph clustering method. We classified 3,199 subjects from twelve different cancer types into five clusters.
GlobalSIP.pdf
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about DICTIONARY LEARNING FOR SPARSE REPRESENTATION USING WEIGHTED L1-NORM
- Log in to post comments
An efficient algorithm for overcomplete dictionary learning with l_p-norm as sparsity constraint to achieve sparse representation from a set of known signals is presented in this paper. The special importance of the l_p-norm (0<p<1) has been recognized in recent studies on sparse modeling, which can lead to stronger sparsity-promoting solutions than the l_1-norm. The l_p-norm, however, leads to a nonconvex optimization problem that is difficult to solve efficiently.
GSIPPOSTER.pdf
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views
- Read more about A ROBUST APPLICATION DETECTOR FOR INTELLIGENT WIRELESS COLLABORATION
- Log in to post comments
We present an approach for detecting application level protocols over a wireless communications link, without the need for demodulation or decryption. Our detector is suitable for diverse radio types, since only simple external signal features are used as inputs. We show that the Profile Hidden Markov Model (PHMM) is well suited to this task, due to the probabilistic nature of the wireless channel and the discrete nature of application level traffic. We include results evaluating the detection performance for two application protocols in 802.11 in the presence of background traffic.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about Image Compression via Multiple Learned Geometric Dictionaries
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views