
ICASSP is the world's largest and most comprehensive technical conference on signal processing and its applications. It provides a fantastic networking opportunity for like-minded professionals from around the world. ICASSP 2017 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers and cutting-edge session topics. Visit ICASSP 2017
- Read more about DIRICHLET PROCESS MIXTURE MODELS FOR CLUSTERING I-VECTOR DATA
- Log in to post comments
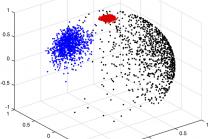
Non-parametric Bayesian methods have recently gained popularity in several research areas dealing with unsupervised learning. These models are capable of simultaneously learning the cluster models as well as their number based on properties of a dataset. The most commonly applied models are using Dirichlet process priors and Gaussian models, called as Dirichlet process Gaussian mixture models (DPGMMs). Recently, von Mises-Fisher mixture models (VMMs) have also been gaining popularity in modelling high-dimensional unit-normalized features such as text documents and gene expression data.
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views- Read more about SUPERPIXEL-GUIDED CFAR DETECTION OF SHIPS AT SEA IN SAR IMAGERY
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views- Read more about Improving Music Source Separation based on DNNs through Data Augmentation and Network Blending
- Log in to post comments
This paper deals with the separation of music into individual instrument tracks which is known to be a challenging problem. We describe two different deep neural network architectures for this task, a feed-forward and a recurrent one, and show that each of them yields themselves state-of-the art results on the SiSEC DSD100 dataset. For the recurrent network, we use data augmentation during training and show that even simple separation networks are prone to overfitting if no data augmentation is used.
- Categories:
 82 Views
82 ViewsThe paper introduces a novel class of complex nonlinear filters, the complex functional link polynomial (CFLiP) filters.
These filters present many interesting properties. They are a sub-class of linear-in-the-parameter nonlinear filters.
They satisfy all the conditions of Stone-Weirstrass theorem and thus are universal approximators for causal, time-invariant, discrete-time, finite-memory, complex, continuous systems defined on a compact domain.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views- Read more about First-Person Action Recognition Through Visual Rhythm Texture Description
- Log in to post comments
First-person action recognition is a recent problem in computer vision, where an observer wears body cameras to understand and recognize actions from the captured video sequences. Technological advances have made it possible to offer small wearable cameras that can be attached onto bike helmets, belts, animal halters, among other accessories. Examples of potential applications include sports, security, healthcare, visual lifelogging, among others.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 1 Views
1 Views- Read more about Optimal Transmit Strategy for MIMO Channels with Joint Sum and Per-antenna Power Constraints
- Log in to post comments
This paper studies optimal transmit strategies for multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) Gaussian channels with joint sum and per-antenna power constraints. It is shown that if an unconstraint optimal allocation for an antenna exceeds a per-antenna power constraint, then the maximal power for this antenna is used in the constraint optimal transmit strategy. This observation is then used in an iterative algorithm to compute the optimal transmit strategy in closed-form. Finally, a numerical example is provided to illustrate the theoretical results.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views- Read more about AN ACCURATE METHOD FOR FREQUENCY ESTIMATION OF A REAL SINUSOID
- Log in to post comments
It is well known that the positive- and negative frequency components of a real sinusoid spectrally interact with each other; thus, introducing bias in frequency estimation based on the periodogram maximization. We propose to filter out the negative-frequency component. To that end, a coarse frequency estimation is obtained using the windowing approach, known to reduce the estimation bias, and then used to filter out the negative frequency component via modulation and discrete Fourier transform
- Categories:
 55 Views
55 Views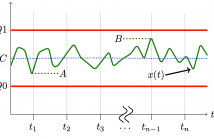
- Read more about INDUCED BIAS IN ATTENUATION MEASUREMENTS TAKEN FROM COMMERCIAL MICROWAVE LINKS
- Log in to post comments
Cellular backhaul networks usually consist of commercial microwave links, known to be sensitive to weather conditions. The management network systems usually provide records of measurements of the transmitted and the received signals levels from the different microwave links for monitoring and analyzing the network performance. Many of them log only the minimum and the maximum levels of the transmitted and the received signals in pre-set intervals (usually 15-minute). Moreover, only quantized version of these measurements are logged.
JO_ICASSP2017.pdf
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views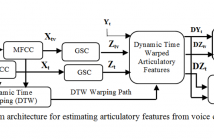
- Read more about QUALITY ASSESSMENT OF VOICE CONVERTED SPEECH USING ARTICULATORY FEATURES
- Log in to post comments
We propose a novel application of the acoustic- to- articulatory inversion (AAI) towards a quality assessment of the voice converted speech. The ability of humans to speak effortlessly requires the coordinated movements of various articulators, muscles, etc. This effortless movement contributes towards a naturalness, intelligibility and speaker’s identity (which is partially present in voice converted speech). Hence, during voice conversion (VC), the information related to the speech production is lost.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views- Read more about Speech Activity Detection in Online Broadcast Transcription Using Deep Neural Networks and Weighted Finite State Transducers
- Log in to post comments
A new approach to online Speech Activity Detection (SAD) is proposed. This approach is designed for the use in a system that carries out 24/7 transcription of radio/TV broadcasts containing a large amount of non-speech segments. To improve the robustness of detection, we adopt Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) trained on artificially created mixtures of speech and non-speech signals at desired levels of Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR). An integral part of our approach is an online decoder based on Weighted Finite State Transducers (WFSTs); this decoder smooths the output from DNN.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views