
ICASSP is the world's largest and most comprehensive technical conference on signal processing and its applications. It provides a fantastic networking opportunity for like-minded professionals from around the world. ICASSP 2017 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers and cutting-edge session topics. Visit ICASSP 2017

- Read more about Low Light Image Enhancement Based on Two-Step Noise Suppression
- Log in to post comments
In low light condition, the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is low and thus the captured images are seriously degraded by noise.Since low light images contain much noise in flat and dark regions, contrast enhancement without considering noise characteristics causes serious noise amplification. In this paper, we propose low light image enhancement based on two-step noise suppression. First, we perform noise aware contrast enhancement using noise level function (NLF).
- Categories:
 50 Views
50 Views- Read more about FAST SPECTRAL CLUSTERING WITH EFFICIENT LARGE GRAPH CONSTRUCTION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 48 Views
48 Views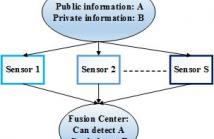
- Read more about MULTILAYER SENSOR NETWORK FOR INFORMATION PRIVACY
- Log in to post comments
A sensor network wishes to transmit information to a fusion center to allow it to detect a public hypothesis, but at the same time prevent it from inferring a private hypothesis. We propose a multilayer sensor network structure, where each sensor first applies a nonlinear fusion function on the information it receives from sensors in a previous layer, and then a linear weighting matrix to distort the information it sends to sensors in the next layer.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 ViewsIn this paper, we propose a novel sparse common spatial pattern (CSP) algorithm to optimally select channels of EEG signals. Compared to the traditional CSP, which maximizes the variance of signals in one class and minimizes the variance of signals in the other class,the classification accuracy is guaranteed by a constraint that the ratio
of variances of signals in two different classes is lower bounded.Then, a sparse spatial filter is achieved by minimizing the l1-norm of filter coefficients and channels of EEG signals can be further optimized.
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views- Read more about FAST HEVC INTRA CODING ALGORITHM BASED ON MACHINE LEARNING AND LAPLACIAN TRANSPARENT COMPOSITE MODEL
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views- Read more about BIOLOGICALLY INSPIRED SPEECH EMOTION RECOGNITION
- Log in to post comments
Conventional feature-based classification methods do not apply well to automatic recognition of speech emotions, mostly because the precise set of spectral and prosodic features that is required to identify the emotional state of a speaker has not been determined yet. This paper presents a method that operates directly on the speech signal, thus avoiding the problematic step of feature extraction.
- Categories:
 48 Views
48 Views- Read more about MULTI-VIEW REPRESENTATION LEARNING VIA GCCA FOR MULTIMODAL ANALYSIS OF PARKINSON'S DISEASE
- Log in to post comments
Information from different bio--signals such as speech, handwriting, and gait have been used to monitor the state of Parkinson's disease (PD) patients, however, all the multimodal bio--signals may not always be available. We propose a method based on multi-view representation learning via generalized canonical correlation analysis (GCCA) for learning a representation of features extracted from handwriting and gait that can be used as a complement to speech--based features. Three different problems are addressed: classification of PD patients vs.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views