
The International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), sponsored by the IEEE Signal Processing Society, is the premier forum for the presentation of technological advances and research results in the fields of theoretical, experimental, and applied image and video processing. ICIP has been held annually since 1994, brings together leading engineers and scientists in image and video processing from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about MARGIN-EMBEDDING CANONICAL CORRELATION ANALYSIS WITH FEATURE SELECTION FOR PERSON RE-IDENTIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
Canonical correlation analysis (CCA) is a classical subspace learning method of capturing the common semantic information underlying multi-view data. It has been used in person re-identification (re-ID) task by treating the task of matching identical individuals across non-overlapping multi-cameras as a multi-view learning problem. However, CCA-based re-ID methods still achieve unsatisfactory results because few jointly consider discriminative margin information and selecting importantly relevant features.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about SYMMETRY-BASED GRAPH FOURIER TRANSFORMS FOR IMAGE REPRESENTATION
- Log in to post comments
It is well-known that the application of the Discrete Cosine Transform
(DCT) in transform coding schemes is justified by the fact that
it belongs to a family of transforms asymptotically equivalent to the
Karhunen-Loève Transform (KLT) of a first order Markov process.
However, when the pixel-to-pixel correlation is low the DCT does
not provide a compression performance comparable with the KLT.
In this paper, we propose a set of symmetry-based Graph Fourier
Transforms (GFT) whose associated graphs present a totally or partially
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views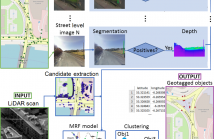
Abundant image and sensory data collected over the last decades represents an invaluable source of information for cataloging and monitoring of the environment. Fusion of heterogeneous data sources is a challenging but promising tool to efficiently leverage such information. In this work we propose a pipeline for automatic detection and geolocation of recurring stationary objects deployed on fusion scenario of street level imagery and LiDAR point cloud data. The objects are geolocated coherently using a fusion procedure formalized as a Markov random field problem.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views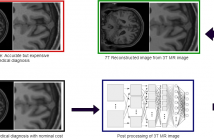
- Read more about MR-SRNET: TRANSFORMATION OF LOW FIELD MR IMAGES TO HIGH FIELD MR IMAGES
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
Most outdoor vision systems can be influenced by rainy weather conditions. In this paper, we address a rain removal problem from a single image. Some existing de-raining methods suffer from hue change due to neglect of the information in low frequency layer. Others fail in assuming enough rainy image models. To solve them, we propose a residual deep network architecture called ResDerainNet. Based on the deep convolutional neural network (CNN), we learn the mapping relationship between rainy and residual images from data.
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views
Most outdoor vision systems can be influenced by rainy weather conditions. In this paper, we address a rain removal problem from a single image. Some existing de-raining methods suffer from hue change due to neglect of the information in low frequency layer. Others fail in assuming enough rainy image models. To solve them, we propose a residual deep network architecture called ResDerainNet. Based on the deep convolutional neural network (CNN), we learn the mapping relationship between rainy and residual images from data.
- Categories:
 44 Views
44 Views
- Read more about MULTICLASS WEIGHTED LOSS FOR INSTANCE SEGMENTATION OF CLUTTERED CELLS
- Log in to post comments
We propose a new multiclass weighted loss function for instance segmentation of cluttered cells. We are primarily motivated by the need of developmental biologists to quantify and model the behavior of blood T-cells which might help us in understanding their regulation mechanisms and ultimately help researchers in their quest for developing an effective immunotherapy cancer treatment.
postericip.pdf
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about ITERATIVE OPTIMIZATION OF QUARTER SAMPLING MASKS FOR NON-REGULAR SAMPLING SENSORS
- Log in to post comments
Non-regular sampling can reduce aliasing at the expense of noise.
Recently, it has been shown that non-regular sampling can be carried
out using a conventional regular imaging sensor when the surface of
its individual pixels is partially covered. This technique is called
quarter sampling (also 1/4 sampling), since only one quarter of each
pixel is sensitive to light. For this purpose, the choice of a proper
sampling mask is crucial to achieve a high reconstruction quality. In
the scope of this work, we present an iterative algorithm to improve
- Categories:
 55 Views
55 Views
- Read more about MULTI-EXPOSURE IMAGE FUSION BASED ON INFORMATION-THEORETIC CHANNEL
- Log in to post comments
We propose a method for multi-exposure image fusion based on information-theoretic channel. In the fusion scheme, conditional entropy, as an information measurement of each pixel in one image to the other image, is calculated through an information channel built between two source images, and then weight maps of the source images are generated. Based on the pyramid scheme, images at every scale are fused by weight maps, and a final fused image is inversely reconstructed.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about A MATRIX-FREE RECONSTRUCTION METHOD FOR COMPRESSIVE FOCAL PLANE ARRAY IMAGING
- Log in to post comments
In this study, we propose a novel algorithm for compressive imaging using digital micromirror device (DMD) modulated focal plane array (FPA) data. In this setting, DMD modulates the scene in the image domain by blocking some of the pixels at a higher resolution level. For reconstruction, a regularized optimization problem is solved, whereas reconstruction time is crucial for a practical compressive sensing application.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views