
The International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), sponsored by the IEEE Signal Processing Society, is the premier forum for the presentation of technological advances and research results in the fields of theoretical, experimental, and applied image and video processing. ICIP has been held annually since 1994, brings together leading engineers and scientists in image and video processing from around the world. Visit website.
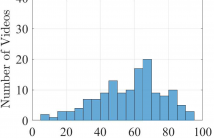
High Dynamic Range (HDR) Wide Color Gamut (WCG) Ultra High Definition (4K/UHD) content has become increasingly popular recently. Due to the increased data rate, novel video compression methods have been developed to maintain the quality of the videos being delivered to consumers under bandwidth constraints. This has led to new challenges for the development of objective Video Quality Assessment (VQA) models, which are traditionally designed without sufficient calibration and validation based on subjective quality assessment of UHD-HDR-WCG videos.
- Categories:
 89 Views
89 Views
- Read more about TRANSFER LEARNING OF Wi-Fi HANDWRITTEN SIGNATURE SIGNALS FOR IDENTITY VERIFICATION BASED ON THE KERNEL AND THE RANGE SPACE PROJECTION
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a system for identity verification based on the gesture signals of handwritten signature captured by the Wi-Fi CSI wave packets at different positions using transfer learning. Essentially, a ConvNet is first pretrained using the Wi-Fi signature signals collected from one position. Subsequently, the pretrained feature extractor is transferred to recognize signals collected from another position via a rapid retraining process. We utilize the kernel and the range space projection learning when we retrain the transferred model.
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
- Read more about poster of "joint image restoration and matching based on hierarchical sparse representation"
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about EFFICIENT SCREEN CONTENT CODING BASED ON CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORK GUIDED BY A LARGE-SCALE DATABASE
- Log in to post comments
Screen content videos (SCVs) are becoming popular in many applications. Compared with natural content videos (NCVs), the SCVs have different characteristics. Therefore, the screen content coding (SCC) based on HEVC adopts some new coding tools (intra block copy and palette mode etc.) to improve coding efficiency, but these tools increase the computational complexity as well. In this paper, we propose to predict the CU partition of the SCVs by a convolutional neural network
- Categories:
 51 Views
51 Views
- Read more about Two images comparison with invariance to illumination properties
- Log in to post comments
A new way of performing pixel by pixel comparison between two images is proposed, taking advantage of interesting invariance properties with respect to illumination conditions and camera settings.
- Categories:
 57 Views
57 Views
- Read more about Spatial and Angular Reconstruction of Light field Based on Deep Generative Networks
- Log in to post comments
Light field (LF) cameras often have significant limitations in spatial and angular resolutions due to their design. Many techniques that attempt to reconstruct LF images at a higher resolution only consider either spatial or angular resolution, but not both. We propose a generative network using high-dimensional convolution to improve both aspects. Our experimental results on both synthetic and real-world data demonstrate that the proposed model outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in terms of both peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and visual quality.
- Categories:
 52 Views
52 Views
- Read more about High-Resolution Class Activation Mapping
- Log in to post comments
Insufficient reasoning for their predictions has for long been a major drawback of neural networks and has proved to be a major obstacle for their adoption by several fields of application. This paper presents a framework for discriminative localization, which helps shed some light into the decision-making of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN). Our framework generates robust, refined and high-quality Class Activation Maps, without impacting the CNN’s performance.
- Categories:
 136 Views
136 Views
- Read more about Estimation of correspondent trajectories in multiple overlapping synchronized videos using correlation of activity functions
- Log in to post comments
We present an approach for ranking a collection of videos with overlapping fields of view. The ranking depends on how they allow to visualize as best as possible, i.e. with significant details, a trajectory query drawn in one of the videos. The proposed approach decomposes each video into cells and aims at estimating a correspondence map between cells from different videos using the linear correlation between their functions of activity.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about Towards Unsupervised Single Image Dehazing with Deep Learning
- Log in to post comments
Deep learning computation is often used in single-image dehazing techniques for outdoor vision systems. Its development is restricted by the difficulties in providing a training set of degraded and ground-truth image pairs. In this paper, we develop a novel model that utilizes cycle generative adversarial network through unsupervised learning to effectively remove the requirement of a haze/depth data set. Qualitative and quantitative experiments demonstrated that the proposed model outperforms existing state-of-the-art dehazing models when tested on both synthetic and real haze images.
- Categories:
 96 Views
96 Views
- Read more about Image smoothing via gradient sparsity and surface area minimization
- Log in to post comments
Image smoothing is a very important topic in image processing. Among these image smoothing methods, the $L_0$ gradient minimization method is one of the most popular ones. However, the $L_0$ gradient minimization method suffers from the staircasing effect and over-sharpening issue, which highly degrade the quality of the smoothed image. To overcome these issues, we use not only the $L_0$ gradient term for finding edges, but also a surface area based term for the purpose of smoothing the inside of each region.
- Categories:
 54 Views
54 Views