
The International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), sponsored by the IEEE Signal Processing Society, is the premier forum for the presentation of technological advances and research results in the fields of theoretical, experimental, and applied image and video processing. ICIP has been held annually since 1994, brings together leading engineers and scientists in image and video processing from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about A 3D FACE MODELING APPROACH FOR IN-THE-WILD FACIAL EXPRESSION RECOGNITION ON IMAGE DATASETS
- Log in to post comments
This paper explores the benefits of 3D face modeling for in-the-wild facial expression recognition (FER). Since there is limited in-the-wild 3D FER dataset, we first construct 3D facial data from available 2D dataset using recent advances in 3D face reconstruction. The 3D facial geometry representation is then extracted by deep learning technique. In addition, we also take advantage of manipulating the 3D face, such as using 2D projected images of 3D face as additional input for FER. These features are then fused with that of 2D FER typical network.
- Categories:
 82 Views
82 Views
- Read more about KPSNET: KEYPOINT DETECTION AND FEATURE EXTRACTION FOR POINT CLOUD REGISTRATION
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents the KPSNet, a KeyPoint Siamese Network to simultaneously learn task-desirable keypoint detector and feature extractor. The keypoint detector is optimized to predict a score vector, which signifies the probability of each candidate being a keypoint. The feature extractor is optimized to learn robust features of keypoints by exploiting the correspondence between the keypoints generated from two inputs, respectively. For training, the KPSNet does not require to manually annotate keypoints and local patches pairwise.
- Categories:
 82 Views
82 Views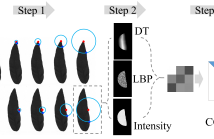
This paper presents a novel shape descriptor to effectively and efficiently characterize the local image statistics. The proposed descriptor, termed contour covariance (CC), characterizes covariance features driven by a moving point on the shape contour at multiple scales. To calculate the covariance matrices, three basic features including texture, intensity and distance map, are extracted from the object image. Based on coefficients of the obtained covariance matrices, the proposed CC descriptor is compact yet informative, as well as invariant to rotation, translation and scale.
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views- Read more about Poster of SDSEN: Self-Refining Deep Symmetry Enhanced Network for Rain Removal
- Log in to post comments
Rain removal aims to remove the rain streaks on rain images. The state-of-the-art methods are mostly based on Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). However, as CNN is not equivariant to object rotation, these methods are unsuitable for dealing with the tilted rain streaks. To tackle this problem, we propose Deep Symmetry Enhanced Network (DSEN) that is able to explicitly extract the rotation equivariant features from rain images. In addition, we design a self-refining mechanism to remove the accumulated rain streaks in a coarse-to-fine manner.
- Categories:
 44 Views
44 Views
- Read more about Glidar3DJ: A VIEW-INVARIANT GAIT IDENTIFICATION VIA FLASH LIDAR DATA CORRECTION
- Log in to post comments
Gait recognition is a leading remote-based identification method, suitable for applications in forensic cases, surveillance, and medical studies. We present Glidar3DJ, a model-based gait recognition methodology, using a skeleton model extracted from sequences generated by a single flash lidar camera. Compared with Kinect, a flash lidar camera has a drastically extended range (> 1000 meters) and its performance is not affected in outdoor.
- Categories:
 79 Views
79 Views
- Read more about LCUTS: LINEAR CLUSTERING OF BACTERIA USING RECURSIVE GRAPH CUTS
- Log in to post comments
Bacterial segmentation poses significant challenges due to
lack of structure, poor imaging resolution, limited contrast
between touching cells and high density of cells that overlap.
Although there exist bacterial segmentation algorithms in the
existing art, they fail to delineate cells in dense biofilms,
especially in 3D imaging scenarios in which the cells are growing
and subdividing in an unstructured manner. A graph-based
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about FAST: Flow-Assisted Shearlet Transform for Densely-sampled Light Field Reconstruction
- Log in to post comments
Shearlet Transform (ST) is one of the most effective methods for Densely-Sampled Light Field (DSLF) reconstruction from a Sparsely-Sampled Light Field (SSLF). However, ST requires a precise disparity estimation of the SSLF. To this end, in this paper a state-of-the-art optical flow method, i.e. PWC-Net, is employed to estimate bidirectional disparity maps between neighboring views in the SSLF. Moreover, to take full advantage of optical flow and ST for DSLF reconstruction, a novel learning-based method, referred to as Flow-Assisted Shearlet Transform (FAST), is proposed in this paper.
- Categories:
 57 Views
57 Views
- Read more about LEARNING GEOGRAPHICALLY DISTRIBUTED DATA FOR MULTIPLE TASKS USING GENERATIVE ADVERSARIAL NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
We present a novel method that supports the learning of multiple classification tasks from geographically distributed data. By combining locally trained generative adversarial networks (GANs) with a small fraction of original data samples, our proposed scheme can train multiple discriminative models at a central location with low communication overhead. Experiments using common image datasets (MNIST, CIFAR-10, LSUN-20, Celeb-A) show that our proposed scheme can achieve comparable classification accuracy as the ideal classifier trained using all data from all sites.
poster-v1.pdf
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views
Image collections, if critical aspects of image content are exposed, can spur research and practical applications in many domains. Supervised machine learning may be the only feasible way to annotate very large collections. However, leading approaches rely on large samples of completely and accurately annotated images. In the case of a large forensic collection that we are aiming to annotate, neither the complete annotation nor the large training samples can be feasibly produced. We, therefore, investigate ways to assist manual annotation efforts done by forensic experts.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about PERSON-SPECIFIC JOY EXPRESSION SYNTHESIS WITH GEOMETRIC METHOD
- Log in to post comments
Smiling has a psychiatric effect in emotional state and may hold tremendous potential for clinical remediation in psychiatric disorders. A few researchers in image synthesis work on acting on the emotional state of subjects by automatically deforming their faces to synthesize joyful expression. However, to generate these expressions they apply the same deformation for the subjects while each person smiles differently. In this paper, we head towards a personalized synthesis of the joy expression.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views