
The International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), sponsored by the IEEE Signal Processing Society, is the premier forum for the presentation of technological advances and research results in the fields of theoretical, experimental, and applied image and video processing. ICIP has been held annually since 1994, brings together leading engineers and scientists in image and video processing from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about Evaluating Crowd Density Estimators via Their Uncertainty Bounds
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about A LIGHTWEIGHT NEURAL NETWORK FOR CROWD ANALYSIS OF IMAGES WITH CONGESTED SCENES
- Log in to post comments
For images with congested scenes, the task of crowd analysis,
including crowd counting and crowd distribution prediction,
becomes very difficult. To address these issues, various
CNN-based approaches have been proposed. However, those
methods usually have a large number of parameters and require
huge computing resources. In this paper, we focus on
low-complexity approaches and propose a lightweight endto-
end network for crowd analysis. Our method utilizes an
effective scale-aware module to extract multi-scale features
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views- Read more about TENSOR-FACTORIZATION-BASED 3D SINGLE IMAGE SUPER-RESOLUTION WITH SEMI-BLIND POINT SPREAD FUNCTION ESTIMATION
- Log in to post comments
A volumetric non-blind single image super-resolution technique using tensor factorization has been recently introduced by our group. That method allowed a 2-order-of-magnitude faster high-resolution image reconstruction with equivalent image quality compared to state-of-the-art algorithms. In this work a joint alternating recovery of the high-resolution image and of the unknown point spread function parameters is proposed. The method is evaluated on dental computed tomography images.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about Dense Optical Flow for the Reconstruction of Weakly Textured and Structured Surfaces: Application to Endoscopy
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about Estimation of Multiple Atmospheric Pollutants Through Image Analysis
- Log in to post comments
Multiple atmospheric pollutants, such as PM2.5, PM10, and NO2, degrades air quality in many parts of the world. Fine-grained air pollution data can help combat the problem, but conventional monitoring stations are too expensive to support high spatial resolution; image-based estimates have the potential to improve spatial coverage. We estimate pollutant concentrations from images using the position-and color-dependent properties of scattering and absorption. We are the first to use images to estimate pollutant concentrations in systems with multiple pollutants.
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views
- Read more about Dense Optical Flow for the Reconstruction of Weakly Textured and Structured Surfaces: Application to Endoscopy
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
This paper introduces a structure from motion (SfM)-based surface reconstruction method for images including weak textures and structures. In SfM, the quality of the determination of homologous points between images plays a key role in terms of reconstruction performances. However, classical feature matching-based methods as integrated in the state-of-the-art SfM algorithms are often inoperative for images with weak structures and textures. This contribution describes a dense optical flow-based solution enabling the point correspondence determination in such scenes.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about Dense Optical Flow for the Reconstruction of Weakly Textured and Structured Surfaces: Application to Endoscopy
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
This paper introduces a structure from motion (SfM)-based surface reconstruction method for images including weak textures and structures. In SfM, the quality of the determination of homologous points between images plays a key role in terms of reconstruction performances. However, classical feature matching-based methods as integrated in the state-ofthe-art SfM algorithms are often inoperative for images with weak structures and textures. This contribution describes a dense optical flow-based solution enabling the point correspondence determination in such scenes.
- Categories:
 45 Views
45 Views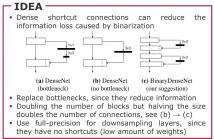
Binary neural networks are a promising approach to execute convolutional neural networks on devices with low computational power. Previous work on this subject often quantizes pretrained full-precision models and uses complex training strategies. In our work, we focus on increasing the performance of binary neural networks by training from scratch with a simple training strategy. In our experiments we show that we are able to achieve state-of-the-art results on standard benchmark datasets.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 64 Views
64 Views
- Read more about DEPRESSION DETECTION BASED ON REACTION TIME AND EYE MOVEMENT
- Log in to post comments
Depression is a common mental disorder, which greatly affects the patients' daily life and work. Current depression detection relies almost exclusively on the clinical interview and structured questionnaire, consuming a lot of medical resources and risking a range of subjective biases. Our goal is to achieve a convenient and objective depression detection system, which can assist clinicians in their diagnosis of clinical depression.
- Categories:
 87 Views
87 Views
- Read more about NMF-based Comprehensive Latent Factor Learning with Multiview Data
- Log in to post comments
Multiview representations reveal the latent information of the data from different perspectives, consistency, and complementarity. Unlike most multiview learning approaches, which focus only one perspective, in this paper, we propose a novel unsupervised multiview learning algorithm, called comprehensive latent factor learning (CLFL), which jointly exploits both consistent and complementary information among multiple views. CLFL adopts a non-negative matrix factorization based formulation to learn the latent factors.
- Categories:
 87 Views
87 Views