
The International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), sponsored by the IEEE Signal Processing Society, is the premier forum for the presentation of technological advances and research results in the fields of theoretical, experimental, and applied image and video processing. ICIP has been held annually since 1994, brings together leading engineers and scientists in image and video processing from around the world. Visit website.

Visual tracking is a very important and challenging problem in the field of computer vision. In recent years, Siamese networks have been widely used for visual tracking due to their fast tracking speed, but many trackers based on Siamese network train their networks by utilizing either pairwise loss or triplet loss, which easily leads to over-fitting. In addition, it is difficult to distinguish some hard samples in the training samples. In this paper, we propose a novel global similarity loss to train the network.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about Kernel Mean p Power Error Loss for Robust Two-Dimensional Singular Value Decomposition
- Log in to post comments
Traditional matrix-based dimensional reduction methods, e.g., two-dimensional principal component analysis (2DPCA) and two-dimensional singular value decomposition (2DSVD), minimize mean square errors (MSE), which is sensitive to outliers. To overcome this problem, in this paper we propose a new robust 2DSVD method based on the kernel mean $p$ power error loss (KMPE-2DSVD).
ICIP20192DSVD.pdf
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views
- Read more about Robust Sparse Learning Based on Kernel Non-second Order Minimization
- Log in to post comments
Partial occlusions in face images pose a great problem for most face recognition algorithms due to the fact that most of these algorithms mainly focus on solving a second order loss function, e.g., mean square error (MSE), which will magnify the effect from occlusion parts. In this paper, we proposed a kernel non-second order loss function for sparse representation (KNS-SR) to recognize or restore partially occluded facial images, which both take the advantages of the correntropy and the non-second order statistics measurement.
ICIP2019sparse.pdf
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about Augmented Visual-semantic Embeddings for Image and Sentence Matching
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views
- Read more about CONTEXT AGGREGATION NETWORK FOR SEMANTIC LABELING IN AERIAL IMAGES
- Log in to post comments
Multi-scale object recognition and accurate object localization are two major problems for semantic segmentation in high resolution aerial images. To handle these problems, we design a Context Fuse Module to aggregate multi-scale features and propose an Attention Mix Module to combine different level features for higher localization accuracy. We further employ a Residual Convolutional Module to refine features in all levels. Based on these modules, we construct a new end-to-end network for semantic labeling in aerial images.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about A dual attention dilated residual network for liver lesion classification and localization on CT images
- Log in to post comments
Automatic liver lesion classification on computed
tomography images is of great importance to early cancer
diagnosis and remains a challenging task. State-of-the-art
liver lesion classification algorithms are currently based on
manually selected regions of interest (ROIs) or automatically
detected ROIs. However, liver lesions usually vary in size
and shape, which makes the ROI selection process laborintensive
and also poses an obstacle to automatic lesion
detection. In this paper, we propose a dual-attention dilated
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views
- Read more about A dual attention dilated residual network for liver lesion classification and localization on CT images
- Log in to post comments
Automatic liver lesion classification on computed
tomography images is of great importance to early cancer
diagnosis and remains a challenging task. State-of-the-art
liver lesion classification algorithms are currently based on
manually selected regions of interest (ROIs) or automatically
detected ROIs. However, liver lesions usually vary in size
and shape, which makes the ROI selection process laborintensive
and also poses an obstacle to automatic lesion
detection. In this paper, we propose a dual-attention dilated
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about A dual attention dilated residual network for liver lesion classification and localization on CT images
- Log in to post comments
Automatic liver lesion classification on computed
tomography images is of great importance to early cancer
diagnosis and remains a challenging task. State-of-the-art
liver lesion classification algorithms are currently based on
manually selected regions of interest (ROIs) or automatically
detected ROIs. However, liver lesions usually vary in size
and shape, which makes the ROI selection process laborintensive
and also poses an obstacle to automatic lesion
detection. In this paper, we propose a dual-attention dilated
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about Loss Switching Fusion with Similarity Search for Video Classification
- Log in to post comments
From video streaming to security and surveillance applications , video data play an important role in our daily living today. However, managing a large amount of video data and retrieving the most useful information for the user remain a challenging task. In this paper, we propose a novel video classification system that would benefit the scene understanding task. We define our classification problem as classifying background and foreground motions using the same feature representation for outdoor scenes.
- Categories:
 140 Views
140 Views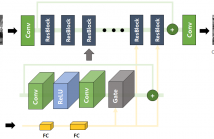
- Read more about ADAPTIVELY TUNING A CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORK BY GATING PROCESS FOR IMAGE DENOISING
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views