
ICIP 2020 is a fully virtual conference. The International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), sponsored by the IEEE Signal Processing Society, is the premier forum for the presentation of technological advances and research results in the fields of theoretical, experimental, and applied image and video processing. ICIP has been held annually since 1994, brings together leading engineers and scientists in image and video processing from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about A BAND ATTENTION AWARE ENSEMBLE NETWORK FOR HYPERSPECTRAL OBJECT TRACKING
- Log in to post comments
Hyperspectral videos contain images with a large number of light wavelength indexed bands that can facilitate material
identification for object tracking. Most hyperspectral trackers use hand-crafted features rather than deep learning gener-
ated features for image representation due to limited training samples. To fill this gap, this paper introduces a band atten-
tion aware ensemble network (BAE-Net) for deep hyperspectral object tracking, which takes advantages of deep models
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views
- Read more about EMPIRICAL ANALYSIS OF OVERFITTING AND MODE DROP IN GAN TRAINING
- Log in to post comments
We examine two key questions in GAN training, namely overfitting and mode drop, from an empirical perspective. We show that when stochasticity is removed from the training procedure, GANs can overfit and exhibit almost no mode drop. Our results shed light on important characteristics of the GAN training procedure. They also provide evidence against prevailing intuitions that GANs do not memorize the training set, and that mode dropping is mainly due to properties of the GAN objective rather than how it is optimized during training.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about EMOTION TRANSFORMATION FEATURE: NOVEL FEATURE FOR DECEPTION DETECTION IN VIDEOS
- Log in to post comments
Deception detection has been a hot research topic in many areas such as jurisprudence, law enforcement, business, and computer vision. However, there are still many problems that are worth more investigation. One of the major challenges is the data scarcity problem. So far, only one multi-modal benchmark dataset on deception detection has been published, which contains 121 video clips for deception detection (61 for deceptive class and 60 for truthful class).
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about Identity-invariant Facial Landmark Frontalization for Facial Expression Analysis
- Log in to post comments
We propose a frontalization technique for 2D facial land- marks, designed to aid in the analysis of facial expressions. It employs a new normalization strategy aiming to minimize identity variations, by displacing groups of facial landmarks to standardized locations. The technique operates directly on 2D landmark coordinates, does not require additional feature extraction and as such is computationally light. It achieves considerable improvement over a reference approach, justifying its use as an efficient preprocessing step for facial expression analysis based on geometric features.
- Categories:
 73 Views
73 Views
- Read more about Automatic Region Selection For Objective Sharpness Assessment of Mobile Device Photos
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Mobile devices are the source of a vast majority of digital photos today. Photos taken by mobile devices generally have fairly good visual quality. When evaluating high-quality mobile device photos, people have to manually zoom in to local regions to discern the subtle difference. Understandably, a global objective quality assessment method cannot perform well on such task. Therefore, local region selection is widely recognized as a prerequisite for the following quality evaluation.
ICIPnow.pdf
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about SELECTIVE COMPLEMENTARY FEATURES FOR MULTI-PERSON POSE ESTIMATION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about A Comparative Evaluation of Temporal Pooling Methods for Blind Video Quality Assessment
- Log in to post comments
Many objective video quality assessment (VQA) algorithms include a key step of temporal pooling of frame-level quality scores. However, less attention has been paid to studying the relative efficiencies of different pooling methods on no-reference (blind) VQA. Here we conduct a large-scale comparative evaluation to assess the capabilities and limitations of multiple temporal pooling strategies on blind VQA of user-generated videos. The study yields insights and general guidance regarding the application and selection of temporal pooling models.
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views
- Read more about JOINT IMAGE SUPER-RESOLUTION VIA RECURRENT CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORKS WITH COUPLED SPARSE PRIORS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views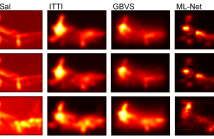
- Read more about DEEP LEARNING VS. TRADITIONAL ALGORITHMS FOR SALIENCY PREDICTION OF DISTORTED IMAGES
- Log in to post comments
Saliency has been widely studied in relation to image quality assessment (IQA). The optimal use of saliency in IQA metrics, however, is nontrivial and largely depends on whether saliency can be accurately predicted for images containing various distortions. Although tremendous progress has been made in saliency modelling, very little is known about whether and to what extent state-of-the-art methods are beneficial for saliency prediction of distorted images.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views