
- Read more about Remixing Music for Hearing Aids Using Ensemble of Fine-Tuned Source Separators
- Log in to post comments
This paper introduces our system submission for the Cadenza ICASSP 2024 Grand Challenge, which presents the problem of remixing and enhancing music for hearing aid users. Our system placed first in the challenge, achieving the best average Hearing-Aid Audio Quality Index (HAAQI) score on the evaluation data set. We describe the system, which uses an ensemble of deep learning music source separators that are fine tuned on the challenge data.
- Categories:
 45 Views
45 Views
- Read more about Unsupervised Speech Enhancement with Diffusion-based Generative Models
- Log in to post comments
Recently, conditional score-based diffusion models have gained significant attention in the field of supervised speech enhancement, yielding state-of-the-art performance. However, these methods may face challenges when generalising to unseen conditions. To address this issue, we introduce an alternative approach that operates in an unsupervised manner, leveraging the generative power of diffusion models.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
- Read more about A Lightweight Hybrid Multi-Channel Speech Extraction System with Directional Voice Activity Detection
- Log in to post comments
Although deep learning (DL) based end-to-end models have shown outstanding performance in multi-channel speech extraction, their practical applications on edge devices are restricted due to their high computational complexity. In this paper, we propose a hybrid system that can more effectively integrate the generalized sidelobe canceller (GSC) and a lightweight post-filtering model under the assistance of spatial speaker activity information provided by a directional voice activity detection (DVAD) module.
- Categories:
 125 Views
125 Views
- Read more about MDX-GAN: ENHANCING PERCEPTUAL QUALITY IN MULTI-CLASS SOURCE SEPARATION VIA ADVERSARIAL TRAINING
- Log in to post comments
Audio source separation aims to extract individual sound sources from an audio mixture. Recent studies on source separation focus primarily on minimizing signal-level distance, typically measured by source-to-distortion ratio (SDR). However, scant attention has been given to the perceptual quality of the separated tracks. In this paper, we propose MDX-GAN, an efficient and high-fidelity audio source separator based on MDX-Net for multiple sound classes. We leverage different training objectives to enhance the perceptual quality of audio source separation.
- Categories:
 50 Views
50 Views
- Read more about General Speech Restoration Using Two-stage Generative Adversarial Networks (slides)
- Log in to post comments
General speech restoration is a challenging task, which requires removing multiple types of distortions within a single system. The prevailing methods for general speech restoration largely rely on generative models, leveraging their ability to generate speech components based on prior knowledge of clean speech characteristics. Our approach adopts a two-stage processing scheme, comprising a speech restoration module and a speech enhancement module. The restoration module utilizes dilated convolutional networks and is trained using LSGAN losses.
- Categories:
 79 Views
79 Views
- Read more about ROTOR NOISE-AWARE NOISE COVARIANCE MATRIX ESTIMATION FOR UNMANNED AERIAL VEHICLE AUDITION
- Log in to post comments
A noise covariance matrix (NCM) estimation method for unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) audition is proposed with rotor noise reduction as its primary focus. The proposed NCM estimation method could be incorporated into audio processing algorithms using UAV-mounted microphone array systems.
- Categories:
 72 Views
72 Views
- Read more about MossFormer2: Combining Transformer and RNN-Free Recurrent Network for Enhanced Time-Domain Monaural Speech Separation
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Our previously proposed MossFormer has achieved promising performance in monaural speech separation. However, it predominantly adopts a self-attention-based MossFormer module, which tends to emphasize longer-range, coarser-scale dependencies, with a deficiency in effectively modelling finer-scale recurrent patterns. In this paper, we introduce a novel hybrid model that provides the capabilities to model both long-range, coarse-scale dependencies and fine-scale recurrent patterns by integrating a recurrent module into the MossFormer framework.
- Categories:
 66 Views
66 Views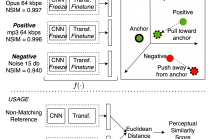
- Read more about NOMAD: Non-Matching Audio Distance
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents NOMAD (Non-Matching Audio Distance), a differentiable perceptual similarity metric that measures the distance of a degraded signal against non-matching references. The proposed method is based on learning deep feature embeddings via a triplet loss guided by the Neurogram Similarity Index Measure (NSIM) to capture degradation intensity. During inference, the similarity score between any two audio samples is computed through Euclidean distance of their embeddings. NOMAD is fully unsupervised and can be used in general perceptual audio tasks for audio analysis e.g.
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
- Read more about Parameter Estimation Procedures for Deep Multi-Frame MVDR Filtering for Single-Microphone Speech Enhancement
- Log in to post comments
Aiming at exploiting temporal correlations across consecutive time frames in the short-time Fourier transform (STFT) domain, multi-frame algorithms for single-microphone speech enhancement have been proposed, which apply a complex- valued filter to the noisy STFT coefficients. Typically, the multi-frame filter coefficients are either estimated directly using deep neural networks or a certain filter structure is imposed, e.g., the multi-frame minimum variance distortionless response (MFMVDR) filter structure.
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views
- Read more about FSPEN: An Ultra-Lightweight Network for Real Time Speech Enhancement
- Log in to post comments
Deep learning-based speech enhancement methods have shown promising result in recent years. However, in practical applications, the model size and computational complexity are important factors that limit their use in end-products. Therefore, in products that require real-time speech enhancement with limited resources, such as TWS headsets, hearing aids, IoT devices, etc., ultra-lightweight models are necessary. In this paper, an ultra-lightweight network FSPEN is proposed for real-time speech enhancement task.
poster.pptx
- Categories:
 106 Views
106 Views