
- Read more about Bandwidth Extension is All You Need
- Log in to post comments
Speech generation and enhancement have seen recent breakthroughs in quality thanks to deep learning. These methods typically operate at a limited sampling rate of 16-22kHz due to computational complexity and available datasets. This limitation imposes a gap between the output of such methods and that of high-fidelity (≥44kHz) real-world audio applications. This paper proposes a new bandwidth extension (BWE) method that expands 8-16kHz speech signals to 48kHz. The method is based on a feed-forward WaveNet architecture trained with a GAN-based deep feature loss.
- Categories:
 134 Views
134 Views
- Read more about Don't shoot butterfly with rifles: Multi-channel Continuous Speech Separation with Early Exit Transformer
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 144 Views
144 Views
- Read more about Continuous Speech Separation with Conformer
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 158 Views
158 Views
- Read more about Enhancement of Ambisonics Signals using time-frequency masking
- Log in to post comments
slides.pdf
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about COMPLEX RATIO MASKING FOR SINGING VOICE SEPARATION
- Log in to post comments
Music source separation is important for applications such as karaoke and remixing. Much of previous research
focuses on estimating magnitude short-time Fourier transform (STFT) and discarding phase information. We observe that,
for singing voice separation, phase has the potential to make considerable improvement in separation quality. This paper
proposes a complex-domain deep learning method for voice and accompaniment separation. The proposed method employs
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about ADL-MVDR: All deep learning MVDR beamformer for target speech separation
- Log in to post comments
Speech separation algorithms are often used to separate the target speech from other interfering sources. However, purely neural network based speech separation systems often cause nonlinear distortion that is harmful for automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems. The conventional mask-based minimum variance distortionless response (MVDR) beamformer can be used to minimize the distortion, but comes with high level of residual noise.
ICASSP Poster 1240.pdf
ICASSP slides 1240.pdf
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
- Read more about Exploiting Non-negative Matrix Factorization for Binaural Sound Localization in the Presence of Directional Interference
- Log in to post comments
This study presents a novel solution to the problem of binaural localization of a speaker in the presence of interfering directional noise and reverberation. Using a state-of-the-art binaural localization algorithm based on a deep neural network (DNN), we propose adding a source separation stage based on non-negative matrix factorization (NMF) to improve the localization performance in conditions with interfering sources.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Autoregressive Fast Multichannel Nonnegative Matrix Factorization For Joint Blind Source Separation And Dereverberation
- Log in to post comments
This paper describes a joint blind source separation and dereverberation method that works adaptively and efficiently in a reverberant noisy environment. The modern approach to blind source separation (BSS) is to formulate a probabilistic model of multichannel mixture signals that consists of a source model representing the time-frequency structures of source spectrograms and a spatial model representing the inter-channel covariance structures of source images.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views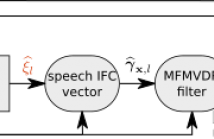
- Read more about Deep Multi-Frame MVDR Filtering for Single-Microphone Speech Enhancement -- Slides
- Log in to post comments
Multi-frame algorithms for single-microphone speech enhancement, e.g., the multi-frame minimum variance distortionless response (MFMVDR) filter, are able to exploit speech correlation across adjacent time frames in the short-time Fourier transform (STFT) domain. Provided that accurate estimates of the required speech interframe correlation vector and the noise correlation matrix are available, it has been shown that the MFMVDR filter yields a substantial noise reduction while hardly introducing any speech distortion.
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views