
- Read more about A STUDY OF MULTICHANNEL SPATIOTEMPORAL FEATURES AND KNOWLEDGE DISTILLATION ON ROBUST TARGET SPEAKER EXTRACTION
- Log in to post comments
Target speaker extraction (TSE) based on direction of arrival (DOA) has a wide range of applications in e.g., remote conferencing, hearing aids, in-car speech interaction. Due to the inherent phase uncertainty, existing TSE methods usually suffer from speaker confusion within specific frequency bands. Imprecise DOA measurements caused by e.g., the calibration of the microphone array and ambient noises, can also deteriorate the TSE performance.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about Noise-Aware Speech Separation with Contrastive Learning
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Recently, speech separation (SS) task has achieved remarkable progress driven by deep learning technique. However, it is still challenging to separate target speech from noisy mixture, as the neural model is vulnerable to assign background noise to each speaker. In this paper, we propose a noise-aware SS (NASS) method, which aims to improve the speech quality for separated signals under noisy conditions. Specifically, NASS views background noise as an additional output and predicts it along with other speakers in a mask-based manner.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
- Read more about Virtual Bass Enhancement via Music Demixing
- Log in to post comments
Virtual Bass Enhancement (VBE) refers to a class of digital signal processing algorithms that aim at enhancing the perception of low frequencies in audio applications. Such algorithms typically exploit well-known psychoacoustic effects and are particularly valuable for improving the performance of small-size transducers often found in consumer electronics. Though both time- and frequency-domain techniques have been proposed in the literature, none of them capitalizes on the latest achievements of deep learning as far as music processing is concerned.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about DIFFUSION-BASED SPEECH ENHANCEMENT WITH JOINT GENERATIVE AND PREDICTIVE DECODERS
- Log in to post comments
Diffusion-based generative speech enhancement (SE) has recently received attention, but reverse diffusion remains time-consuming. One solution is to initialize the reverse diffusion process with enhanced features estimated by a predictive SE system. However, the pipeline structure currently does not consider for a combined use of generative and predictive decoders. The predictive decoder allows us to use the further complementarity between predictive and diffusion-based generative SE.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about RVAE-EM: Generative Speech Dereverberation Based On Recurrent Variational Auto-Encoder And Convolutive Transfer Function
- Log in to post comments
In indoor scenes, reverberation is a crucial factor in degrading the perceived quality and intelligibility of speech. In this work, we propose a generative dereverberation method. Our approach is based on a probabilistic model utilizing a recurrent variational auto-encoder (RVAE) network and the convolutive transfer function (CTF) approximation. Different from most previous approaches, the output of our RVAE serves as the prior of the clean speech.
posterA0.pdf
- Categories:
 37 Views
37 Views
- Read more about SLIDES - Real-Time Multichannel Speech Separation And Enhancement Using A Beamspace-Domain-Based Lightweight CNN
- Log in to post comments
The problems of speech separation and enhancement concern the extraction of the speech emitted by a target speaker when placed in a scenario where multiple interfering speakers or noise are present, respectively. A plethora of practical applications such as home assistants and teleconferencing require some sort of speech separation and enhancement pre-processing before applying Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) systems. In the recent years, most techniques have focused on the application of deep learning to either time-frequency or time-domain representations of the input audio signals.
- Categories:
 42 Views
42 Views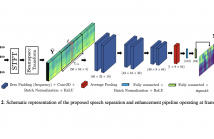
- Read more about PAPER - Real-Time Multichannel Speech Separation And Enhancement Using A Beamspace-Domain-Based Lightweight CNN
- Log in to post comments
The problems of speech separation and enhancement concern the extraction of the speech emitted by a target speaker when placed in a scenario where multiple interfering speakers or noise are present, respectively. A plethora of practical applications such as home assistants and teleconferencing require some sort of speech separation and enhancement pre-processing before applying Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) systems. In the recent years, most techniques have focused on the application of deep learning to either time-frequency or time-domain representations of the input audio signals.
- Categories:
 50 Views
50 Views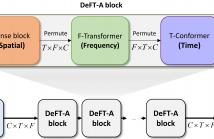
- Read more about DeFT-AN: Dense Frequency-Time Attentive Network for Multichannel Speech Enhancement
- Log in to post comments
In this study, we propose a dense frequency-time attentive network (DeFT-AN) for multichannel speech enhancement. DeFT-AN is a mask estimation network that predicts a complex spectral masking pattern for suppressing the noise and reverberation embedded in the short-time Fourier transform (STFT) of an input signal. The proposed mask estimation network incorporates three different types of blocks for aggregating information in the spatial, spectral, and temporal dimensions.
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
- Read more about SELECTIVE MUTUAL LEARNING: AN EFFICIENT APPROACH FOR SINGLE CHANNEL SPEECH SEPARATION
- Log in to post comments
Mutual learning, the related idea to knowledge distillation, is a group of untrained lightweight networks, which simultaneously learn and share knowledge to perform tasks together during training. In this paper, we propose a novel mutual learning approach, namely selective mutual learning. This is the simple yet effective approach to boost the performance of the networks for speech separation. There are two networks in the selective mutual learning method, they are like a pair of friends learning and sharing knowledge with each other.
- Categories:
 184 Views
184 Views
- Read more about ICASSP - Sequential MCMC methods for audio signal enhancement
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
With the aim of addressing audio signal restoration as a sequential inference problem, we build upon Gabor regression to propose a state-space model for audio time series. Exploiting the structure of our model, we devise a sequential Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithm to explore the sequence of filtering distributions of the synthesis coefficients. The algorithm is then tested on a series of denoising examples.
- Categories:
 55 Views
55 Views