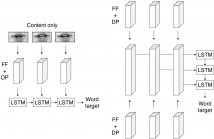
We present a novel lipreading system that improves on the task of speaker-independent word recognition by decoupling motion and content dynamics. We achieve this by implementing a deep learning architecture that uses two distinct pipelines to process motion and content and subsequently merges them, implementing an end-to-end trainable system that performs fusion of independently learned representations. We obtain a average relative word accuracy improvement of ≈6.8% on unseen speakers and of ≈3.3% on known speakers, with respect to a baseline which uses a standard architecture.
- Categories:
 53 Views
53 Views
- Read more about Adaptation of an EMG-Based Speech Recognizer via Meta-Learning
- Log in to post comments
In nonacoustic speech recognition based on electromyography, i.e. on electrical muscle activity captured by noninvasive surface electrodes, differences between recording sessions are known to cause deteriorating system accuracy. Efficient adaptation of an existing system to an unseen recording session is therefore imperative for practical usage scenarios. We report on a meta-learning approach to pretrain a deep neural network frontend for a myoelectric speech recognizer in a way that it can be easily adapted to a new session.
- Categories:
 186 Views
186 Views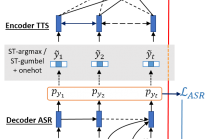
- Read more about END-TO-END FEEDBACK LOSS IN SPEECH CHAIN FRAMEWORK VIA STRAIGHT-THROUGH ESTIMATOR
- Log in to post comments
The speech chain mechanism integrates automatic speech recognition (ASR) and text-to-speech synthesis (TTS) modules into a single cycle during training. In our previous work, we applied a speech chain mechanism as a semi-supervised learning. It provides the ability for ASR and TTS to assist each other when they receive unpaired data and let them infer the missing pair and optimize the model with reconstruction loss.
- Categories:
 72 Views
72 Views
- Read more about Subword Regularization and Beam Search Decoding for End-to-End Automatic Speech Recognition
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we experiment with the recently introduced subword regularization technique \cite{kudo2018subword} in the context of end-to-end automatic speech recognition (ASR). We present results from both attention-based and CTC-based ASR systems on two common benchmark datasets, the 80 hour Wall Street Journal corpus and 1,000 hour Librispeech corpus. We also introduce a novel subword beam search decoding algorithm that significantly improves the final performance of the CTC-based systems.
- Categories:
 46 Views
46 Views
- Read more about ACOUSTICALLY GROUNDED WORD EMBEDDINGS FOR IMPROVED ACOUSTICS-TO-WORD SPEECH RECOGNITION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views
- Read more about LANGUAGE MODEL INTEGRATION BASED ON MEMORY CONTROL FOR SEQUENCE TO SEQUENCE SPEECH RECOGNITION
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we explore several new schemes to train a seq2seq model to integrate a pre-trained language model (LM). Our proposed fusion methods focus on the memory cell state and the hidden state in the seq2seq decoder long short-term memory (LSTM), and the memory cell state is updated by the LM unlike the prior studies. This means the memory retained by the main seq2seq would be adjusted by the external LM.
Final_final.pdf
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views- Read more about Sequence-to-Sequence ASR Optimization via Reinforcement Learning
- Log in to post comments
Despite the success of sequence-to-sequence approaches in automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems, the models still suffer from several problems, mainly due to the mismatch between the training and inference conditions. In the sequence-to-sequence architecture, the model is trained to predict the grapheme of the current time-step given the input of speech signal and the ground-truth grapheme history of the previous time-steps. However, it remains unclear how well the model approximates real-world speech during inference.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about End-to-End Multimodal Speech Recognition
- Log in to post comments
Transcription or sub-titling of open-domain videos is still a chal- lenging domain for Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) due to the data’s challenging acoustics, variable signal processing and the essentially unrestricted domain of the data. In previous work, we have shown that the visual channel – specifically object and scene features – can help to adapt the acoustic model (AM) and language model (LM) of a recognizer, and we are now expanding this work to end-to-end approaches.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views- Read more about AN INVESTIGATION INTO INSTANTANEOUS FREQUENCY ESTIMATION METHODS FOR IMPROVED SPEECH RECOGNITION FEATURES
- Log in to post comments
There have been several studies, in the recent past, pointing to the
importance of analytic phase of the speech signal in human percep-
tion, especially in noisy conditions. However, phase information is
still not used in state-of-the-art speech recognition systems. In this
paper, we illustrate the importance of analytic phase of the speech
signal for automatic speech recognition. As the computation of ana-
lytic phase suffers from inevitable phase wrapping problem, we ex-
tract features from its time derivative, referred to as instantaneous
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about Comparison of DCT and Autoencoder-based Features for DNN-HMM Multimodal Silent Speech Recognition
- Log in to post comments
poster-llc.pdf
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views