- Image/Video Storage, Retrieval
- Image/Video Processing
- Image/Video Coding
- Image Scanning, Display, and Printing
- Image Formation
- Read more about Dcitionary Learning for Poisson Compressed Sensing
- Log in to post comments
Imaging techniques involve counting of photons striking a detector. Due to fluctuations in the counting process, the measured photon counts are known to be corrupted by Poisson noise. In this paper, we propose a blind dictionary learning framework for the reconstruction of photographic image data from Poisson corrupted measurements acquired by a \emph{compressive} camera.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views- Read more about DICTIONARY LEARNING FOR POISSON COMPRESSED SENSING
- Log in to post comments
Imaging techniques involve counting of photons striking a detector.
Due to fluctuations in the counting process, the measured
photon counts are known to be corrupted by Poisson
noise. In this paper, we propose a blind dictionary learning
framework for the reconstruction of photographic image data
from Poisson corrupted measurements acquired by a compressive
camera. We exploit the inherent non-negativity of the
data by modeling the dictionary as well as the sparse dictionary
coefficients as non-negative entities, and infer these directly
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
Color pixel encoding optimizes the conversion of linear physical values of light into integer values. The efficiency of such encoding methods depends on a trade-off between the bit-depth used and the visible distortion introduced by quantization. This efficiency for different color pixel encoding approaches has been evaluated in literature, without considering the fact that before transmission to the end-user, color encoded content needs to be compressed using a video codec.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
- Read more about Subjective and Objective Quality Assessment of Tone- Mapped Images
- Log in to post comments
1570165825.pdf
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about Face Image Quality Assessment for Face Selection in Surveillance Video using Convolutional Neural Networks
- Log in to post comments
1570165667.pdf
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about Eccentricity Effect of Motion Silencing on Naturalistic Videos
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views- Read more about Locally Linear Low-rank Tensor Approximation
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views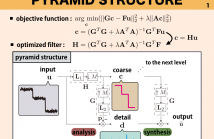
- Read more about Edge Preserving Multiscale Image Decomposition with Customized Domain Transform Filters
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, a multiscale image decomposition method based on domain transform is proposed. The domain transform is a high speed edge preserving smoothing method and can be used to many image processing applications. However, it is highly sensitive to noise. The proposed method is based on filters used in the domain transform but is designed to be robust to noise by employing a multiscale method. An optimization problem is formulated to obtain desired domain- transformed output. As expected, the method can be used to many applications as the domain transform.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views