- Image/Video Storage, Retrieval
- Image/Video Processing
- Image/Video Coding
- Image Scanning, Display, and Printing
- Image Formation
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views- Read more about Simulation of grain growth in polycrystalline materials: A signal processing perspective
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views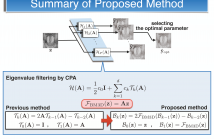
- Read more about Globalized BM3D using fast eigenvalue filtering
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 81 Views
81 ViewsIn this work, we propose an improved fast multiple-view image denoising algorithm using 3D focus image stacks. It showed improved computational efficiency and comparable denoising quality compared to conventional methods.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
Presentation slides covering:
- robust foreground detection / background subtraction via patch-based analysis
- person re-identification based on representations on Riemannian manifolds
- robust object tracking via Grassmann manifolds
- adapting the lessons from big data to computer vision
- future paradigm shifts: computer vision based on networks of neurosynaptic cores
- Categories:
 62 Views
62 Views
Slides from the Tutorial on Riemannian Geometry in Computer Vision, presented at the Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV), Singapore, 2014.
The slides show (1) how objects can be interpreted as points on Riemannian and Grassmann manifolds, and (2) various distance measures on manifolds. Demonstrates usefulness of manifold techniques in applications such as object tracking and person re-identification.
- Categories:
 85 Views
85 Views
For the purposes of foreground estimation, the true background model is unavailable in many practical circumstances and needs to be estimated from cluttered image sequences. We propose a sequential technique for static background estimation in such conditions, with low computational and memory requirements. Image sequences are analysed on a block-by-block basis. For each block location a representative set is maintained which contains distinct blocks obtained along its temporal line.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Article Summaries - SPM Special Issue on Signal Processing for Art Investigation
- Log in to post comments
Expanded version of the Guest Editorial
for Special Issue on Signal Processing for Art Investigation
(IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, July 2015)
Include short summaries for each of the 11 articles in the special issue.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views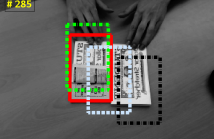
We propose an adaptive tracking algorithm where the object is modelled as a continuously updated bag of affine subspaces, with each subspace constructed from the object's appearance over several consecutive frames. In contrast to linear subspaces, affine subspaces explicitly model the origin of subspaces. Furthermore, instead of using a brittle point-to-subspace distance during the search for the object in a new frame, we propose to use a subspace-to-subspace distance by representing candidate image areas also as affine subspaces.
report.pdf
- Categories:
 40 Views
40 Views
- Read more about Reduced-Reference Structural Quality Assessment for Retargeted Images
- Log in to post comments
Recent years have witnessed tremendous growth in the generation and consumption of digital images. Monitoring and evaluating image quality is an important issue for online and mobile media applications. Conventional quality assessment work mostly focus on intensity level distortion caused by operations that do not change image aspect ratio/size, such as distortion caused by compression, noise, and blurring. Here, we study the problem of quality assessment for images undergone content-adaptive resizing, also known as retargeting operations.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views