
- Read more about SAM-OCTA: A Fine-Tuning Strategy for Applying Foundation Model OCTA Image Segmentation Tasks
- Log in to post comments
In the analysis of optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) images, the operation of segmenting specific targets is necessary. Existing methods typically train on supervised datasets with limited samples (approximately a few hundred), which can lead to overfitting. To address this, the low-rank adaptation technique is adopted for foundation model fine-tuning and proposed corresponding prompt point generation strategies to process various segmentation tasks on OCTA datasets. This method is named SAM-OCTA and has been experimented on the publicly available OCTA-500 dataset.
- Categories:
 37 Views
37 Views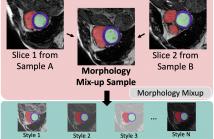
- Read more about MMS: Morphology-mixup Stylized Data Generation for Single Domain Generalization in Medical Image Segmentation
- Log in to post comments
Single-source domain generalization in medical image segmentation is a challenging yet practical task, as domain shift commonly exists across medical datasets.
Previous works have attempted to alleviate this problem through adversarial data augmentation or random-style transformation.
However, these approaches neither fully leverage medical information nor consider the morphological structure alterations.
To address these limitations and enhance the fidelity and diversity of the augmented data,
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views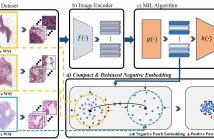
- Read more about COMPACT AND DE-BIASED NEGATIVE INSTANCE EMBEDDING FOR MULTI-INSTANCE LEARNING ON WHOLE-SLIDE IMAGE CLASSIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
Whole-slide image (WSI) classification is a challenging task because 1) patches from WSI lack annotation, and 2) WSI possesses unnecessary variability, e.g., stain protocol. Recently, Multiple-Instance Learning (MIL) has made significant progress, allowing for classification based on slide-level, rather than patch-level, annotations. However, existing MIL methods ignore that all patches from normal slides are normal. Using this free annotation, we introduce a semi-supervision signal to de-bias the inter-slide variability and to capture the common factors of variation within normal patches.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views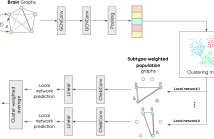
- Read more about Subtype-specific biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease from anatomical and functional connectomes via graph neural networks
- Log in to post comments
Heterogeneity is present in Alzheimer’s disease (AD), making it challenging to study. To address this, we propose a graph neural network (GNN) approach to identify disease subtypes from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and functional MRI (fMRI) scans. Subtypes are identified by encoding the patients’ scans in brain graphs (via cortical similarity networks) and clustering the representations learnt by the GNN.
- Categories:
 46 Views
46 Views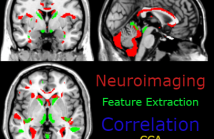
- Read more about MULTIMODAL IMAGING FEATURE EXTRACTION WITH REFERENCE CANONICAL CORRELATION ANALYSIS UNDERLYING INTELLIGENCE
- Log in to post comments
With neuroimaging data scientists have gained substantial information on the neuronal underpinning of intelligence. Yet how to integrate multimodal neuronal features effectively in relation to intelligence remains elusive. In this paper, we have developed a reference Canonical Correlation Analysis (RCCA) model that extracts latent, correlated multimodal features while enhancing correlation to a reference of interest.
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views
- Read more about RESIDUAL DENSE SWIN TRANSFORMER FOR CONTINUOUS DEPTH-INDEPENDENT ULTRASOUND IMAGING
- Log in to post comments
Ultrasound imaging is crucial for evaluating organ morphology and function, yet depth adjustment can degrade image quality and field-of-view, presenting a depth-dependent dilemma. Traditional interpolation-based zoom-in techniques often sacrifice detail and introduce artifacts. Motivated by the potential of arbitrary-scale super-resolution to naturally address these inherent challenges, we present the Residual Dense Swin Transformer Network (RDSTN), designed to capture the non-local characteristics and long-range dependencies intrinsic to ultrasound images.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about EARLY DIAGNOSING PARKINSON'S DISEASE VIA A DEEP LEARNING MODEL BASED ON AUGMENTED FACIAL EXPRESSION DATA
- Log in to post comments
It is crucial to promptly diagnose potential Parkinson's disease (PD) patients in order to facilitate early treatment and prevent disease progression. In recent years, there has been growing interest in using facial expressions for in-vitro PD diagnosis due to the distinct "masked face" characteristics of PD patients and the cost-effectiveness of this approach. However, current facial expression-based PD diagnosis methods are hindered by limited training data on PD patients' facial expressions and weak prediction models.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views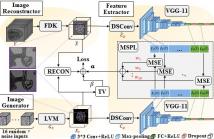
- Read more about STABLE OPTIMIZATION FOR LARGE VISION MODEL BASED DEEP IMAGE PRIOR IN CONE-BEAM CT RECONSTRUCTION
- Log in to post comments
Large Vision Model (LVM) has recently demonstrated great potential for medical imaging tasks, potentially enabling image enhancement for sparse-view Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT), despite requiring a substantial amount of data for training. Meanwhile, Deep Image Prior (DIP) effectively guides an untrained neural network to generate high-quality CBCT images without any training data. How- ever, the original DIP method relies on a well-defined forward model and a large-capacity backbone network, which is no- toriously difficult to converge.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 40 Views
40 Views
- Read more about BLIND INPAINTING WITH OBJECT-AWARE DISCRIMINATION FOR ARTIFICIAL MARKER REMOVAL
- Log in to post comments
Medical images often incorporate doctor-added markers that can hinder AI-based diagnosis. This issue highlights the need of inpainting techniques to restore the corrupted visual contents. However, existing methods require manual mask annotation as input, limiting the application scenarios. In this paper, we propose a novel blind inpainting method that automatically reconstructs visual contents within the corrupted regions without mask input as guidance. Our model includes a blind reconstruction network and an object-aware discriminator for adversarial training.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about Enhancing Generalization in Medical Visual Question Answering Tasks via Gradient-Guided Model Perturbation
- Log in to post comments
Leveraging pre-trained visual language models has become a widely adopted approach for improving performance in downstream visual question answering (VQA) applications. However, in the specialized field of medical VQA, the scarcity of available data poses a significant barrier to achieving reliable model generalization. Numerous methods have been proposed to enhance model generalization, addressing the issue from data-centric and model-centric perspectives.
poster_lhy.pdf
- Categories:
 42 Views
42 Views