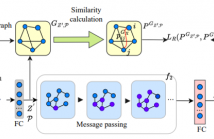
- Read more about Deep Manifold Transformation for Protein Representation Learning
- Log in to post comments
Protein representation learning is critical in various tasks in biology, such as drug design and protein structure or function prediction, which has primarily benefited from protein language models and graph neural networks. These models can capture intrinsic patterns from protein sequences and structures through masking and task-related losses. However, the learned protein representations are usually not well optimized, leading to performance degradation due to limited data, difficulty adapting to new tasks, etc.
- Categories:
 52 Views
52 Views
- Read more about FAST PERSONALIZED TEXT TO IMAGE SYNTHESIS WITH ATTENTION INJECTION
- Log in to post comments
Currently, personalized image generation methods mostly require considerable time to finetune and often overfit the concept resulting in generated images that are similar to custom concepts but difficult to edit by prompts. We propose an effective and fast approach that could balance the text-image consistency and identity consistency of the generated image and reference image. Our method can generate personalized images without any fine-tuning while maintaining the inherent text-to-image generation ability of diffusion models.
- Categories:
 41 Views
41 Views
- Read more about VISUAL ADAPT FOR RGBD TRACKING
- Log in to post comments
Recent RGBD trackers have employed cueing techniques by overlaying Depth modality images as cues onto RGB modality images, which are then fed into the RGB-based model for tracking. However, the direct overlaying interaction method between modalities not only introduces more noise into the feature space but also exhibits the inadaptability of the RGB-based model to mixed-modality inputs. To address these issues, we introduce Visual Adapt for RGBD Tracking (VADT). Specifically, we maintain the input of the RGB-based model as the RGB modality.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views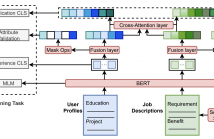
- Read more about TAROT: A Hierarchical Framework with Multitask Co-Pretraining on Semi-Structured Data Towards Effective Person-Job Fit
- Log in to post comments
Person-job fit is an essential part of online recruitment platforms in serving various downstream applications like Job Search and Candidate Recommendation. Recently, pretrained large language models have further enhanced the effectiveness by leveraging richer textual information in user profiles and job descriptions apart from user behavior features and job metadata. However, the general domain-oriented design struggles to capture the unique structural information within user profiles and job descriptions, leading to a loss of latent semantic correlations.
- Categories:
 55 Views
55 Views
Prompt learning was proposed to solve the problem of inconsistency between the upstream and downstream tasks and has achieved State-Of-The-Art (SOTA) results in various Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks. However, Relation Extraction (RE) is more complex than other text classification tasks, which makes it more difficult to design a suitable prompt template for each dataset manually. To solve this issue, we propose a Adaptive Prompt Construction method (APC) for relation extraction.
- Categories:
 98 Views
98 Views
- Read more about HIM: DISCOVERING IMPLICIT RELATIONSHIPS IN HETEROGENEOUS SOCIAL NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
To date, research on relation mining has typically focused on analyzing explicit relationships between entities, while ignoring the underlying connections between entities, known as implicit relationships. Exploring implicit relationships can reveal more about social dynamics and potential relationships in heterogeneous social networks to better explain complex social behaviors. The research presented in this paper explores implicit relationships discovery methods in the context of heterogeneous social networks.
- Categories:
 134 Views
134 Views
- Read more about On the exploitation of DCT-traces in the Generative-AI domain
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Deepfakes represent one of the toughest challenges in the world of Cybersecurity and Digital Forensics, especially considering the high-quality results obtained with recent generative AI-based solutions. Almost all generative models leave unique traces in synthetic data that, if analyzed and identified in detail, can be exploited to improve the generalization limitations of existing deepfake detectors.
- Categories:
 195 Views
195 Views
- Read more about RID-TWIN-Supp
- Log in to post comments
Supplementary material for RID-TWIN: AN END-TO-END PIPELINE FOR AUTOMATIC FACE DE-IDENTIFICATION IN VIDEOS
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about Cloud Detection
- Log in to post comments
This document contains supplementary material which outlines key aspects regarding the dataset creation process, along with the methodology employed for benchmarking state-of-the-art deep leaning models. We aim to provide a clear and comprehensive overview, thus dividing the topic into six fundamental points. Beginning with point one, we delve into the method of data collection and organization, elucidating how the data can be interpreted and utilized. This section is crucial for understanding the origin and nature of the data comprising our dataset.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views