- Read more about Iterative Autoregressive Generation for Abstractive Summarization
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
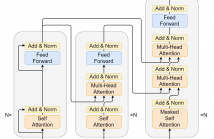
Abstractive summarization suffers from exposure bias caused by the teacher-forced maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) learning, that an autoregressive language model predicts the next token distribution conditioned on the exact pre-context during training while on its own predictions at inference. Preceding resolutions for this problem straightforwardly augment the pure token-level MLE with summary-level objectives.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about psoter 11535
- Log in to post comments
Acoustic-scene-related parameters such as relative transfer functions (RTFs) and power spectral densities (PSDs) of the target source, late reverberation and ambient noise are essential and challenging to estimate. Existing methods typically only estimate a subset of the parameters by assuming the other parameters are known. This can lead to unmatched scenarios and reduced estimation performance. Moreover, many methods process time frames independently, despite they share common information such as the same RTF.
- Categories:
 1 Views
1 Views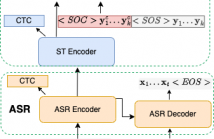
- Read more about Enhancing End-to-End Conversational Speech Translation Through Target Language Context Utilization
- Log in to post comments
Incorporating longer context has been shown to benefit machine translation, but the inclusion of context in end-to-end speech translation (E2E-ST) remains under-studied. To bridge this gap, we introduce target language context in E2E-ST, enhancing coherence and overcoming memory constraints of extended audio segments. Additionally, we propose context dropout to ensure robustness to the absence of context, and further improve performance by adding speaker information. Our proposed contextual E2E-ST outperforms the isolated utterance-based E2E-ST approach.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
- Read more about DBS
- Log in to post comments
Network pruning is an effective technique to reduce computation costs for deep model deployment on resource-constraint devices. Searching superior sub-networks from a vast search space through Neural Architecture Search (NAS) , which conducts a one-shot supernet used as a performance estimator, is still time-consuming. In addition to searching ineffciency, such solutions also focus on FLOPs budget and suffer from an inferior ranking consistency between supernet-inherited and stand-alone performance. To solve the problems above, we propose a framework, namely DBS.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
Modern social media platforms play an important role in facilitating rapid dissemination of information through their massive user networks. Fake news, misinformation, and unverifiable facts on social media platforms propagate disharmony and affect society. In this paper, we consider the problem of misinformation detection which classify news items as fake or real. Specifically, driven by experiential studies on real-world social media platforms, we propose a probabilistic Markovian information spread model over networks modeled by graphs.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about GLAND SEGMENTATION VIA DUAL ENCODERS AND BOUNDARY-ENHANCED ATTENTION
- Log in to post comments
Accurate and automated gland segmentation on pathological images can assist pathologists in diagnosing the malignancy of colorectal adenocarcinoma. However, due to various gland shapes, severe deformation of malignant glands, and overlapping adhesions between glands. Gland segmentation has always been very challenging. To address these problems, we propose a DEA model. This model consists of two branches: the backbone encoding and decoding network and the local semantic extraction network.
- Categories:
 51 Views
51 Views
- Read more about MTA: A Lightweight Multilingual Text Alignment Model for Cross-language Visual Word Sense Disambiguation
- Log in to post comments
Visual Word Sense Disambiguation (Visual-WSD), as a subtask of fine-grained image-text retrieval, requires a high level of language-vision understanding to capture and exploit the nuanced relationships between text and visual features. However, the cross-linguistic background only with limited contextual information is considered the most significant challenges for this task.
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views
- Read more about UNSUPERVISED LEARNING OF NEURAL SEMANTIC MAPPINGS WITH THE HUNGARIAN ALGORITHM FOR COMPOSITIONAL SEMANTICS
- Log in to post comments
Neural semantic parsing maps natural languages (NL) to equivalent formal semantics which are compositional and deduce the sentence meanings by composing smaller parts. To learn a well-defined semantics, semantic parsers must recognize small parts, which are semantic mappings between NL and semantic tokens. Attentions in recent neural models are usually explained as one-on-one semantic mappings. However, attention weights with end-to-end training are shown only weakly correlated with human-labeled mappings. Despite the usefulness, supervised mappings are expensive.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views
- Read more about AdaPlus: Integrating Momentum and Precise Stepsize Adjustment on AdamW Basis
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes an efficient optimizer called AdaPlus which integrates Nesterov momentum and precise stepsize adjustment on AdamW basis. AdaPlus combines the advantages of AdamW, Nadam, and AdaBelief and, in particular, does not introduce any extra hyper-parameters. We perform extensive experimental evaluations on three machine learning tasks to validate the effectiveness of AdaPlus.
ICASSP.pdf
- Categories:
 43 Views
43 Views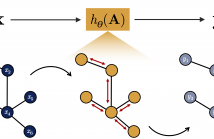
- Read more about Bayesian topology inference on partially known networks from input-output pairs
- Log in to post comments
We propose a sampling algorithm to perform system identification from a set of input-output graph signal pairs. The dynamics of the systems we study are given by a partially known adjacency matrix and a generic parametric graph filter of unknown parameters. The methodology we employ is built upon the principles of annealed Langevin diffusion. This enables us to draw samples from the posterior distribution instead of following the classical approach of point estimation using maximum likelihood.
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views