
- Categories:
 53 Views
53 Views
- Read more about Residual Squeeze-and-Excitation U-shaped Network for Minutia Extraction in Contactless Fingerprint Images
- Log in to post comments
Slides.pdf
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views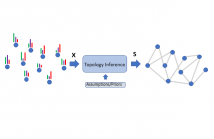
- Read more about Network Topology Inference from Gaussian and Stationary Graph Signals
- Log in to post comments
Graphs have become pervasive tools to represent information and datasets with irregular support. However, in many cases, the underlying graph is either unavailable or naively obtained, calling for more advanced methods for its estimation. Indeed, graph topology inference methods that estimate the network structure from a set of signal observations have a long and well-established history. By assuming that the observations are both Gaussian and stationary in the sought graph, this paper proposes a new scheme to learn the network from nodal observations.
- Categories:
 55 Views
55 Views
- Read more about MaskDUL: Data Uncertainty Learning in Masked Face Recognition
- Log in to post comments
Since mask occlusion causes plentiful loss of facial feature, Masked Face Recognition (MFR) is a challenging image processing task, and the recognition results are susceptible to noise. However, existing MFR methods are mostly deterministic point embedding models, which are limited in representing noise images. Moreover, Data Uncertainty Learning (DUL) fails to achieve reasonable performance in MFR.
Poster.pdf
- Categories:
 50 Views
50 Views
- Read more about Delay-aware Backpressure Routing Using Graph Neural Networks
- Log in to post comments
We propose a throughput-optimal biased backpressure (BP) algorithm for routing, where the bias is learned through a graph neural network that seeks to minimize end-to-end delay. Classical BP routing provides a simple yet powerful distributed solution for resource allocation in wireless multi-hop networks but has poor delay performance. A low-cost approach to improve this delay performance is to favor shorter paths by incorporating pre-defined biases in the BP computation, such as a bias based on the shortest path (hop) distance to the destination.
- Categories:
 54 Views
54 Views
This paper investigates negative sampling for contrastive learning in the context of audio-text retrieval. The strategy for negative sampling refers to selecting negatives (either audio clips or textual descriptions) from a pool of candidates for a positive audio-text pair. We explore sampling strategies via model-estimated within-modality and cross-modality relevance scores for audio and text samples. With a constant training setting on the retrieval system from [1], we study eight sampling strategies, including hard and semi-hard negative sampling.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about Cross-Lingual Transfer Learning for Alzheimer’s Detection from Spontaneous Speech
- Log in to post comments
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease most often associated with memory deficits and cognitive decline. With the aging population, there has been much interest in automated methods for cognitive impairment detection. One approach that has attracted attention in recent years is AD detection through spontaneous speech. While the results are promising, it is not certain whether the learned speech features can be generalized across languages. To fill this gap, the ADReSS-M challenge was organized.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about IQGAN: Robust Quantum Generative Adversarial Network for Image Synthesis On NISQ Devices
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views