
- Read more about SEGMENTATION AND CLASSIFICATION-BASED DIAGNOSIS OF TUMORS FROM BREAST ULTRASOUND IMAGES USING MULTIBRANCH UNET
- Log in to post comments
Breast ultrasound is useful for the diagnosis of breast tumors which can be benign or malignant. However, accurate segmentation of breast tumors and the classification of breast ultrasound into benign, malignant, or normal (no tumor) categories is challenging because of different reasons including poor contrast of the tumor region and absence of clear margins. We propose a Multibranch UNet architecture that uses multitask learning for the automated segmentation of breast tumors and classification of breast ultrasound images.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about AN AUTOMATIC COLORECTAL POLYPS DETECTION APPROACH FOR CT COLONOGRAPHY
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views
- Read more about CLOT: Contrastive Learning-Driven and Optimal Transport-Based Training for Simultaneous Clustering
- Log in to post comments
Clustering via representation learning is one of the most promising approaches for self-supervised learning of deep neural networks. It aims at obtaining artificial supervisory signals from unlabeled data. In this paper, we propose an online clustering method called CLOT (\underline{C}ontrastive \underline{L}earning-Driven and \underline{O}ptimal \underline{T}ransport-Based Clustering) that is based on robust and multiple losses training settings. More specifically, CLOT learns representations by contrasting both the features at the latent space and the cluster assignments.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about DESIGNING STRONG BASELINES FOR TERNARY NEURAL NETWORK QUANTIZATION THROUGH SUPPORT AND MASS EQUALIZATION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views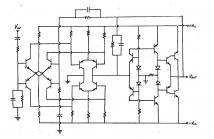
___Although dated, this student thesis is re-published as the proposed negative feedback topology and the current mode arrangement of silicon bipolar junction transistors is rarely elaborated in the many excellent contemporary books on audio power amplifier design.
- Categories:
 80 Views
80 Views
- Read more about A CLUSTERED FEDERATED LEARNING APPROACH FOR ESTIMATING THE QUALITY OF EXPERIENCE OF WEB USERS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about STATISTICAL ANALYSIS OF SPEECH DISORDER SPECIFIC FEATURES TO CHARACTERISE DYSARTHRIA SEVERITY LEVEL
- Log in to post comments
Poor coordination of the speech production subsystems due to any neurological injury or a neuro-degenerative disease leads to dysarthria, a neuro-motor speech disorder. Dysarthric
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views
- Read more about RECOGNIZING HIGHLY VARIABLE AMERICAN SIGN LANGUAGE IN VIRTUAL REALITY
- Log in to post comments
Recognizing signs in virtual reality (VR) is challenging; here, we developed an American Sign Language (ASL) recognition system in a VR environment. We collected a dataset of 2,500 ASL numerical digits (0-10) and 500 instances of the ASL sign for TEA from 10 participants using an Oculus Quest 2. Participants produced ASL signs naturally, resulting in significant variability in location, orientation, duration, and motion trajectory. Additionally, the ten signers in this initial study were diverse in age, sex, ASL proficiency, and hearing status, with most being deaf lifelong ASL users.
- Categories:
 82 Views
82 Views
- Read more about RECOGNIZING HIGHLY VARIABLE AMERICAN SIGN LANGUAGE IN VIRTUAL REALITY
- Log in to post comments
Recognizing signs in virtual reality (VR) is challenging; here, we developed an American Sign Language (ASL) recognition system in a VR environment. We collected a dataset of 2,500 ASL numerical digits (0-10) and 500 instances of the ASL sign for TEA from 10 participants using an Oculus Quest 2. Participants produced ASL signs naturally, resulting in significant variability in location, orientation, duration, and motion trajectory. Additionally, the ten signers in this initial study were diverse in age, sex, ASL proficiency, and hearing status, with most being deaf lifelong ASL users.
SLTAT 2023.pdf
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about F0 ESTIMATION FROM TELEPHONE SPEECH USING DEEP FEATURE LOSS
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Accurate pitch estimation in speech signal plays a vital role in several applications. Robust pitch estimation in telephone speech is still a challenge due to the narrow bandwidth of the signal. Electroglottograph (EGG) signal is a reliable means for pitch estimation, however, it’s not practically possible to
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views