
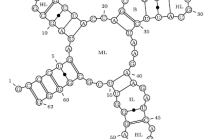
- Read more about RNA secondary structures: from ab initio prediction to better compression, and back
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we use the biological domain knowledge incorporated into stochastic models
for ab initio RNA secondary-structure prediction to improve the state of the art in joint
compression of RNA sequence and structure data (Liu et al., BMC Bioinformatics, 2008).
Moreover, we show that, conversely, compression ratio can serve as a cheap and robust
proxy for comparing the prediction quality of different stochastic models, which may help
guide the search for better RNA structure prediction models.
- Categories:
 37 Views
37 Views
- Read more about Linear Computation Coding: Exponential Search and Reduced-State Algorithms
- Log in to post comments
Linear computation coding is concerned with the compression of multidimensional linear functions, i.e. with reducing the computational effort of multiplying an arbitrary vector to an arbitrary, but known, constant matrix.
This paper advances over the state-of-the art, that is based on a discrete matching pursuit (DMP) algorithm, by a step-wise optimal search.
Offering significant performance gains over DMP, it is however computationally infeasible for large matrices and high accuracy.
dcc23_lcc.pdf
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views- Read more about Practical construction of sensing matrices for a greedy sparse recovery algorithm over finite fields
- Log in to post comments
Compressed sensing aims to retrieve sparse signals from very few samples. It relies on dedicated reconstruction algorithms and well-chosen measurement matrices. In combination with network coding, which operates traditionally over finite fields, it leverages the benefits of both techniques. However, compressed sensing has been primarily investigated over the real field. F2OMP is one of the few recovery algorithms to reconstruct signals over finite fields. However, its use in practical cases is limited since its performance depends mainly on binary matrices for signal recovery.
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views
- Read more about Contextual Pattern Matching in Less Space
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views
Lossless data compression algorithms were developed to shrink files. But these algorithms can also be used to measure file similarity. In this article, the meta-algorithms Concat Compress and Cross Compress are subjected to an extensive practical test together with the compression algorithms Re-Pair, gzip and bz2: Five labeled datasets are subjected to a classification procedure using these algorithms. Theoretical considerations about the two meta-algorithms were already made about 10 years ago, but little has happened since then.
- Categories:
 85 Views
85 Views
- Read more about Storage Constrained Linear Computation Coding
- Log in to post comments
Linear computation coding (LCC) has been developed in as a new framework
for the computation of linear functions. LCC significantly reduces the complexity
of matrix-vector multiplication. In basic LCC, storage is not restricted i.e. the
wiring exponents are arbitrary integer exponents of 2.
In this work, we constrain the set of wiring exponents to be finite. From an
information-theoretic viewpoint, this problem is function compression with a finite-alphabet
representation by atoms. We show that by an efficient choice of this set,
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views
- Categories:
 46 Views
46 Views
End-to-end learned image compression (LIC) has become promising alternatives for lossy image compression. However, deployments of LIC models are restricted, due to excessive network parameters and high computational complexity. Existing LIC models realized throughout with integer networks are significantly degraded in rate-distortion (R-D) performance. In this paper, we propose a novel fully integerized model for LIC that leverages channel-wise weight and activation quantization.
- Categories:
 78 Views
78 Views
- Read more about Mixed-precision Deep Neural Network Quantization With Multiple Compression Rates
- Log in to post comments
Quantization of one deep neural network to multiple compression rates (precisions) has been recently considered for flexible deployments in real-world scenarios. However, existing methods for network quantization under multiple compression rates leverage fixed-precision bit-width allocation or heuristically search for mixed-precision strategy and cannot well balance efficiency and performance.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views