
- Read more about Provable Sample Complexity Guarantees for Learning of Continuous-Action Graphical Games with Nonparametric Utilities
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about Information Theoretic Limits for Standard and One-bit Compressed Sensing with Graph-structured Sparsity
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about Domain Generalized Few-Shot Image Classification Via Meta Regularization Network
- Log in to post comments
1435_poster.pdf
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about Integration of Pre-trained Networks with Continuous Token Interface For End-to-End Spoken Language Understanding
- Log in to post comments
Most End-to-End (E2E) Spoken Language Understanding (SLU) networks leverage the pre-trained Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) networks but still lack the capability to understand the semantics of utterances, crucial for the SLU task. To solve this, recently proposed studies use pre-trained Natural Language Understanding (NLU) networks. However, it is not trivial to fully utilize both pre-trained networks; many solutions were proposed, such as Knowledge Distillation (KD), cross-modal shared embedding, and network integration with Interface.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
- Read more about OPENFEAT: Improving Speaker Identification by Open-set Few-shot Embedding Adaptation with Transformer
- Log in to post comments
Household speaker identification with few enrollment utterances is an important yet challenging problem, especially when household members share similar voice characteristics and room acoustics. A common embedding space learned from a large number of speakers is not universally applicable for the optimal identification of every speaker in a household.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views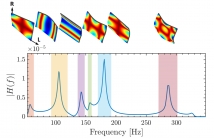
- Read more about On the Prediction of the Frequency Response of a Wooden Plate from its Mechanical Parameters
- Log in to post comments
Inspired by deep learning applications in structural mechanics, we focus on how to train two predictors to model the relation between the vibrational response of a prescribed point of a wooden plate and its material properties. In particular, the eigenfrequencies of the plate are estimated via multilinear regression, whereas their amplitude is predicted by a feedforward neural network.
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
- Read more about Identification of Edge Disconnections in Networks Based on Graph Filter Outputs
- Log in to post comments
Graphs are fundamental mathematical structures used in various fields to model statistical and physical relationships between data, signals, and processes. In some applications, such as data processing in graphs that represent physical networks, the initial network topology is known. However, disconnections of edges in the network change the topology and may affect the signals and processes over the network. In this paper, we consider the problem of edge disconnection identification in networks by using concepts from graph signal processing.
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
- Read more about DIFFICULTY-AWARE NEURAL BAND-TO-PIANO SCORE ARRANGEMENT BASED ON NOTE- AND STATISTIC-LEVEL CRITERIA
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about Light-SERNet: A Lightweight Fully Convolutional Neural Network for Speech Emotion Recognition
- Log in to post comments
Detecting emotions directly from a speech signal plays an important role in effective human-computer interactions. Existing speech emotion recognition models require massive computational and storage resources, making them hard to implement concurrently with other machine-interactive tasks in embedded systems. In this paper, we propose an efficient and lightweight fully convolutional neural network (FCNN) for speech emotion recognition in systems with limited hardware resources.
- Categories:
 37 Views
37 Views