- Read more about REAL-TIME OBJECT DETECTION BY A MULTI-FEATURE FULLY CONVOLUTIONAL NETWORK
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views- Read more about COUPLED ANALYSIS-SYNTHESIS DICTIONARY LEARNING FOR PERSON RE-IDENTIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a novel coupled dictionary learning method, namely coupled analysis-synthesis dictionary learning, to improve the performance of person re-identification in the non-overlapping fields of different camera views. Most of the existing coupled dictionary learning methods train a coupled synthesis dictionary directly on the original feature spaces, which limits the representation ability of the dictionary.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views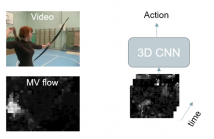
- Read more about COMPRESSED-DOMAIN VIDEO CLASSIFICATION WITH DEEP NEURAL NETWORKS: “THERE’S WAY TOO MUCH INFORMATION TO DECODE THE MATRIX”
- Log in to post comments
We investigate video classification via a 3D deep convolutional neural network (CNN) that directly ingests compressed bitstream information. This idea is based on the observation that video macroblock (MB) motion vectors (that are very compact and directly available from the compressed bitstream) are inherently capturing local spatiotemporal changes in each video scene.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views- Read more about FAST AND ACCURATE IMAGE RECOGNITION USING DEEPLY-FUSED BRANCHY NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
In order to achieve higher accuracy of image recognition, deeper and wider networks have been used. However, when the network size gets bigger, its forward inference time also takes longer. To address this problem, we propose Deeply-Fused Branchy Network (DFB-Net) by adding small but complete side branches to the target baseline main branch. DFB-Net allows easy-to-discriminate samples to be classified faster. For hard-to-discriminate samples, DFB-Net makes probability fusion by averaging softmax probabilities to make collaborative predictions.
- Categories:
 57 Views
57 Views- Read more about Hyper-Parameter Optimization for Convolutional Neural Network Committees Based on Evolutionary Algorithms
- Log in to post comments
In a broad range of computer vision tasks, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are one of the most prominent techniques due to their outstanding performance.
Yet it is not trivial to find the best performing network structure for a specific application because it is often unclear how the network structure relates to the network accuracy.
We propose an evolutionary algorithm-based framework to automatically optimize the CNN structure by means of hyper-parameters.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views- Read more about SSPP-DAN: Deep Domain Adaptation Network for Face Recognition with Single Sample Per Person
- Log in to post comments
Real-world face recognition using a single sample per person (SSPP) is a challenging task. The problem is exacerbated if the conditions under which the gallery image and the probe set are captured are completely different. To address these issues from the perspective of domain adaptation, we introduce an SSPP domain adaptation network (SSPP-DAN). In the proposed approach, domain adaptation, feature extraction, and classification are performed jointly using a deep architecture with domain-adversarial training.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about TOWARDS THINNER CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORKS THROUGH GRADUALLY GLOBAL PRUNING
- Log in to post comments
Deep network pruning is an effective method to reduce the storage and computation cost of deep neural networks when applying them to resource-limited devices. Among many pruning granularity, neuron level pruning will remove redundant neurons and filters in the model and result in thinner networks. In this paper, we propose a gradually global pruning scheme for neuron level pruning. In each pruning step, a small percent of neurons were selected and dropped across all layers in the model.
WangzhengtaoICIP.pdf
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views- Read more about Age Group Classification in the Wild with Deep RoR Architecture
- Log in to post comments
Automatically predicting age group from face images acquired in unconstrained conditions is an important and challenging task in many real-world applications. Nevertheless, the conventional methods with manually-designed features on in-the-wild benchmarks are unsatisfactory because of incompetency to tackle large variations in unconstrained images.
- Categories:
 62 Views
62 Views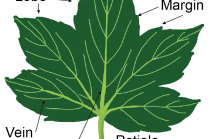
We introduce a new reference axis for leaf classification. The new reference axis, called a Mid-Leaf axis, is based on a quadratic curve that lies on the middle of a leaf. This curve is derived from three basic landmark points: an apex, a centroid, and a petiole. After mapping to a new plane based on this curve, leaf shape features are invariant under translation, rotation, scaling, and bending. We propose the leaf shape features based on partitioning the morphological features and the tangent’s direction angle of the leaf contour.
- Categories:
 63 Views
63 Views