- Read more about 4D Effect Classification by Encoding CNN Features
- Log in to post comments
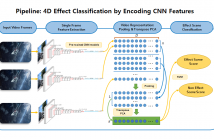
4D effects are physical effects simulated in sync with videos, movies, and games to augment the events occurring in a story or a virtual world. Types of 4D effects commonly used for the immersive media may include seat motion, vibration, flash, wind, water, scent, thunderstorm, snow, and fog. Currently, the recognition of physical effects from a video is mainly conducted by human experts. Although 4D effects are promising in giving immersive experience and entertainment, this manual production has been the main obstacle to faster and wider application of 4D effects.
- Categories:
 40 Views
40 Views- Read more about Integrated Deep and Shallow Networks for Salient Object Detection
- Log in to post comments
icip-ppt.pdf
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views- Read more about A Deep Learning Network for Vision-based Vacant Parking Space Detection System
- Log in to post comments
In the demonstration, we would show our live and real-time parking space detection system. The detection function is founded on a video surveillance system built in an outdoor parking lot. As we might know, it is challenging to implement a practical vision system in an outdoor environment owing to the dramatic lighting changes and uncontrollable variations from weather conditions.
- Categories:
 73 Views
73 Views- Read more about Parking Space Detection Based on A Multi-task Deep Convolutional Network with Spatial Transform
- Log in to post comments
Vacant parking space detection is a challenging vision task due to outdoor lighting variation and perspective distortion. Previous methods found on camera geometry and projection matrix to select space image region for status classification. By utilizing suitable hand-crafted features, outdoor lighting variation and perspective distortion could be well handled. However, if also considering parking displacement, non-unified car size, and inter-object occlusion, we find the problem becomes more troublesome.
- Categories:
 55 Views
55 Views- Read more about Human-human interaction recognition based on spatial and motion trend feature
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views- Read more about NONLINEAR SUBSPACE CLUSTERING
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents a nonlinear subspace clustering (NSC) method for image clustering. Unlike most existing subspace clustering methods which only exploit the linear relationship of samples to learn the affine matrix, our NSC reveals the multi-cluster nonlinear structure of samples via a nonlinear neural network. While kernel-based clustering methods can also address the nonlinear issue of samples, this type of methods suffers from the scalability issue.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views- Read more about HGO-CNN: HYBRID GENERIC-ORGAN CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORK FOR MULTI-ORGAN PLANT CLASSIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
Classification of plants based on a multi-organ approach is very challenging. Although additional data provides more information that might help to disambiguate between species, the variability in shape and appearance in plant organs also raises the degree of complexity of the problem. Existing approaches focus mainly on generic features for species classification, disregarding the features representing the organs. In fact, plants are complex entities sustained by a number of organ systems.
HGO-CNN.pdf
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views- Read more about RANDOM MATRICES MEET MACHINE LEARNING: A LARGE DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS OF LS-SVM
- Log in to post comments
This article proposes a performance analysis of kernel least squares support vector machines (LS-SVMs) based on a random matrix approach, in the regime where both the dimension of data p and their number n grow large at the same rate. Under a two-class Gaussian mixture model for the input data, we prove that the LS-SVM decision function is asymptotically normal with means and covariances shown to depend explicitly on the derivatives of the kernel function. This provides improved understanding along with new insights into the internal workings of SVM-type methods for large datasets.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views- Read more about End to end spoofing detection with raw wave CLDNNs
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views- Read more about Automatic Radar Waveform Recognition Based on Time-Frequency Analysis and Convolutional Neural Network
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 45 Views
45 Views