
- Read more about Kernel Mean p Power Error Loss for Robust Two-Dimensional Singular Value Decomposition
- Log in to post comments
Traditional matrix-based dimensional reduction methods, e.g., two-dimensional principal component analysis (2DPCA) and two-dimensional singular value decomposition (2DSVD), minimize mean square errors (MSE), which is sensitive to outliers. To overcome this problem, in this paper we propose a new robust 2DSVD method based on the kernel mean $p$ power error loss (KMPE-2DSVD).
ICIP20192DSVD.pdf
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views
- Read more about TRANSFER LEARNING OF Wi-Fi HANDWRITTEN SIGNATURE SIGNALS FOR IDENTITY VERIFICATION BASED ON THE KERNEL AND THE RANGE SPACE PROJECTION
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a system for identity verification based on the gesture signals of handwritten signature captured by the Wi-Fi CSI wave packets at different positions using transfer learning. Essentially, a ConvNet is first pretrained using the Wi-Fi signature signals collected from one position. Subsequently, the pretrained feature extractor is transferred to recognize signals collected from another position via a rapid retraining process. We utilize the kernel and the range space projection learning when we retrain the transferred model.
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
- Read more about INDUCTIVE CONFORMAL PREDICTOR FOR SPARSE CODING CLASSIFIERS: APPLICATIONS TO IMAGE CLASSIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
Conformal prediction uses the degree of strangeness (nonconformity) of new data instances to determine the confidence values of new predictions. We propose an inductive conformal predictor for sparse coding classifiers, referred to as ICP-SCC. Our contribution is twofold: first, we present two nonconformitymeasures that produce reliable confidence values; second, we propose a batchmode active learning algorithm within the conformal prediction framework to improve classification performance by selecting training instances based on two criteria, informativeness and diversity.
- Categories:
 37 Views
37 Views
- Read more about TENSOR MATCHED KRONECKER-STRUCTURED SUBSPACE DETECTION FOR MISSING INFORMATION
- Log in to post comments
We consider the problem of detecting whether a tensor signal having many missing entities lies within a given low dimensional Kronecker-Structured (KS) subspace. This is a matched subspace detection problem. Tensor matched subspace detection problem is more challenging because of the intertwined signal dimensions. We solve this problem by projecting the signal onto the KS subspace, which is a Kronecker product of different subspaces corresponding to each signal dimension. Under this framework, we define the KS subspaces and the orthogonal projection of the signal onto the KS subspace.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views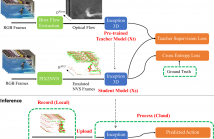
- Read more about NEUROMORPHIC VISION SENSING FOR CNN-BASED ACTION RECOGNITION
- Log in to post comments
Neuromorphic vision sensing (NVS) hardware is now gaining traction as a low-power/high-speed visual sensing technology that circumvents the limitations of conventional active pixel sensing (APS) cameras. While object detection and tracking models have been investigated in conjunction with NVS, there is currently little work on NVS for higher-level semantic tasks, such as action recognition.
- Categories:
 59 Views
59 Views
- Read more about Feature Selection for Multi-labeled Variables via Dependency Maximization
- Log in to post comments
Feature selection and reducing the dimensionality of data is an essential step in data analysis. In this work, we propose a new criterion for feature selection that is formulated as conditional information between features given the labeled variable. Instead of using the standard mutual information measure based on Kullback-Leibler divergence, we use our proposed criterion to filter out redundant features for the purpose of multiclass classification.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about AUTOMATIC RADAR-BASED GESTURE DETECTION VIA REGION-BASED DCNN
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, a region-based deep convolutional neural network
(R-DCNN) is proposed to detect and classify gestures
measured by a frequency-modulated continuous wave radar
system. Micro-Doppler (μD) signatures of gestures are exploited,
and the resulting spectrograms are fed into a neural
network. We are the first to use the R-DCNN for radar-based
gesture recognition, such that multiple gestures could be automatically
detected and classified without manually clipping
the data streams according to each hand movement in advance.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about Recurrent Neural Networks with Stochastic Layers for Acoustic Novelty Detection
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we adapt Recurrent Neural Networks with Stochastic Layers, which are the state-of-the-art for generating text, music and speech, to the problem of acoustic novelty detection. By integrating uncertainty into the hidden states, this type of network is able to learn the distribution of complex sequences. Because the learned distribution can be calculated explicitly in terms of probability, we can evaluate how likely an observation is then detect low-probability events as novel.
- Categories:
 2 Views
2 Views
- Read more about Learning Motion Disfluencies for Automatic Sign Language Segmentation
- Log in to post comments
We introduce a novel technique for the automatic detection of word boundaries within continuous sentence expressions in Japanese Sign Language from three-dimensional body joint positions. First, the flow of signed sentence data within a temporal neighborhood is determined utilizing the spatial correlations between line segments of inter-joint pairs. Next, a frame-wise binary random forest classifier is trained to distinguish word and non-word frame content based on the extracted spatio-temporal features.
Poster.pdf
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views
- Read more about A LARGE SCALE ANALYSIS OF LOGISTIC REGRESSION: ASYMPTOTIC PERFORMANCE AND NEW INSIGHTS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views