- Read more about An Online Feature Selection Architecture For Human Activity Recognition
- Log in to post comments
Human Activity Recognition (HAR) must currently face up to the challenge of rethinking analytics from the perspective of real-time operation, wherein biophysical sensing streams are efficiently intertwined at close vicinity to the point of sensing. As such, feature selection techniques, traditionally employed for off-line data processing, should be evaluated with respect to their ability to filter out redundant information in real-time.
- Categories:
 2 Views
2 Views
- Read more about Part-Level Fully Convolutional Networks for Pedestrian Detection
- Log in to post comments
Since pedestrians in videos have a wide range of appearances such as body poses, occlusions, and complex backgrounds, pedestrian detection is a challengeable task. In this paper, we propose part-level fully convolutional networks (FCN) for pedestrian detection. We adopt deep learning to deal with the proposal shifting problem in pedestrian detection. First, we combine convolutional neural networks (CNN) and FCN to align bounding boxes for pedestrians. Then, we perform part-level pedestrian detection based on CNN to recall the lost body parts.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views- Read more about TWO-STAGE FACIAL AGE PREDICTION USING GROUP-SPECIFIC FEATURES
- Log in to post comments
A novel two-stage age prediction approach with group-specific features is proposed in this paper. Aging process is captured through a highly discriminating feature representation that models shape, appearance, skin spots, and wrinkles. The two-stage method consists of a multi-class Support Vector Machine (SVM) to predict the age bracket while the final age prediction is carried out using Support Vector Regression (SVR). The novelty of our work is that the feature extraction is group-specific and can therefore be tailored to each age bracket in the specific age prediction step.
ICASSP2017.pdf
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views- Read more about Through-the-Wall Radar Signal Classification using Discriminative Dictionary Learning
- Log in to post comments
Through-the-wall radar imaging is an electromagnetic wave sensing technology capable of detecting targets behind walls, doors, and opaque obstacles. Identification of stationary targets is often achieved by first forming an image of the scene, and then segmenting and classifying the targets of interest. In order to provide prompt and reliable situational awareness, this paper proposes a radar signal classification approach that does not rely on image formation.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views- Read more about FAST SPECTRAL CLUSTERING WITH EFFICIENT LARGE GRAPH CONSTRUCTION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 48 Views
48 Views- Categories:
 95 Views
95 Views
- Read more about A ROBUST APPLICATION DETECTOR FOR INTELLIGENT WIRELESS COLLABORATION
- Log in to post comments
We present an approach for detecting application level protocols over a wireless communications link, without the need for demodulation or decryption. Our detector is suitable for diverse radio types, since only simple external signal features are used as inputs. We show that the Profile Hidden Markov Model (PHMM) is well suited to this task, due to the probabilistic nature of the wireless channel and the discrete nature of application level traffic. We include results evaluating the detection performance for two application protocols in 802.11 in the presence of background traffic.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views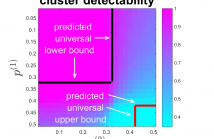
- Read more about Multilayer Spectral Graph Clustering via Convex Layer Aggregation
- Log in to post comments
Multilayer graphs are commonly used for representing different relations between entities and handling heterogeneous data processing tasks. New challenges arise in multilayer graph clustering for assigning clusters to a common multilayer node set and for combining information from each layer. This paper presents a theoretical framework for multilayer spectral graph clustering of the nodes via convex layer aggregation.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about Out-of-label Suppression Dictionary Learning with Cluster Regularization
- Log in to post comments
This paper addresses the problem of learning a discriminative dictionary from training signals. Given a structured dictionary, each atom of which has its corresponding label, one signal should be mainly constructed by its closely associated atoms. Besides the representations for the same class ought to be very close to form a cluster. Thus we present out-of-label suppression dictionary model with cluster regularization to amplify the discriminative power. Upon out-of-label suppression, we don't adopt $l_0$-norm or $l_1$-norm for regularization.
GlobalSIP 2016.pdf
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views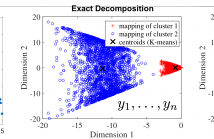
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views