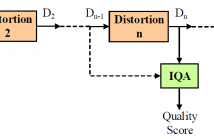
- Read more about Quality Assessment of Images Undergoing Multiple Distortion Stages
- Log in to post comments
In practical media distribution systems, visual content often undergoes multiple stages of quality degradations along the delivery chain between the source and destination. By contrast, current image quality assessment (IQA) models are typically validated on image databases with a single distortion stage. In this work, we construct two large-scale image databases that are composed of more than 2 million images undergoing multiple stages of distortions and examine how state-of-the-art IQA algorithms behave over distortion stages.
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views
High Dynamic Range (HDR) Wide Color Gamut (WCG) Ultra High Definition (4K/UHD) content has become increasingly popular recently. Due to the increased data rate, novel video compression methods have been developed to maintain the quality of the videos being delivered to consumers under bandwidth constraints. This has led to new challenges for the development of objective Video Quality Assessment (VQA) models, which are traditionally designed without sufficient calibration and validation based on subjective quality assessment of UHD-HDR-WCG videos.
- Categories:
 89 Views
89 Views
- Read more about AN EYE-TRACKING DATABASE OF VIDEO ADVERTISING
- Log in to post comments
Reliably predicting where people look in images and videos remains challenging and requires substantial eye-tracking data to be collected and analysed for various applications. In this paper, we present an eye-tracking study where twenty-eight participants viewed forty still scenes of video advertising. First, we analyse human attentional behaviour based on gaze data. Then, we evaluate to what extent a machine – saliency model – can predict human behaviour. Experimental results show that there is a significant gap between human and machine in visual saliency.
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
- Read more about SUBJECTIVE ASSESSMENT OF IMAGE QUALITY INDUCED SALIENCY VARIATION
- Log in to post comments
Our previous study has shown that image distortions cause saliency distraction, and that visual saliency of a distorted image differs from that of its distortion-free reference. Being able to measure such distortion-induced saliency variation (DSV) significantly benefits algorithms for automated image quality assessment. Methods of quantifying DSV, however, remain unexplored due to the lack of a benchmark. In this paper, we build a benchmark for the measurement of DSV through a subjective study.
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
- Read more about BLIND QUALITY EVALUATOR FOR SCREEN CONTENT IMAGES VIA ANALYSIS OF STRUCTURE
- Log in to post comments
Existing blind evaluators for screen content images (SCIs) are mainly learning-based and require a number of training images with co-registered human opinion scores. However, the size of existing databases is small, and it is labor-, timeconsuming and expensive to largely generate human opinion scores. In this study, we propose a novel blind quality evaluator without training.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about Improving Facial Attractiveness Prediction via Co-Attention Learning
- Log in to post comments
Facial attractiveness prediction has drawn considerable attention from image processing community.
Despite the substantial progress achieved by existing works, various challenges remain.
One is the lack of accurate representation for facial composition, which is essential for attractiveness evaluation. In this paper, we propose to use pixel-wise labelling masks as the meta information of facial composition, and input them into a network for learning high-level semantic representations.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views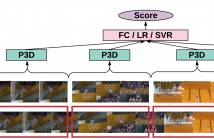
- Read more about S3D: Stacking Segmental P3D for Action Quality Assessment
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Action quality assessment is crucial in areas of sports, surgery and assembly line where action skills can be evaluated. In this paper, we propose the Segment-based P3D-fused network S3D built-upon ED-TCN and push the performance on the UNLV-Dive dataset by a significant margin. We verify that segment-aware training performs better than full-video training which turns out to focus on the water spray. We show that temporal segmentation can be embedded with few efforts.
- Categories:
 105 Views
105 Views
- Read more about PAC-Net: Pairwise Aesthetic Comparison Network For Image Aesthetic Assessment
- Log in to post comments
Image aesthetic assessment is important for finding well taken and appealing photographs but is challenging due to the ambiguity and subjectivity of aesthetic criteria. We develop the pairwise aesthetic comparison network (PAC-Net), which consists of two parts: aesthetic feature extraction and pairwise feature comparison. To alleviate the ambiguity and subjectivity, we train PAC-Net to learn the relative aesthetic ranks of two images by employing a novel loss function, called aesthetic-adaptive cross entropy loss.
- Categories:
 149 Views
149 Views
- Read more about VR IQA NET: Deep Virtual Reality Image Quality Assessment using Adversarial Learning
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a novel virtual reality image quality assessment (VR IQA) with adversarial learning for omnidirectional images. To take into account the characteristics of the omnidirectional image, we devise deep networks including novel quality score predictor and human perception guider. The proposed quality score predictor automatically predicts the quality score of distorted image using the latent spatial and position feature.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views
- Read more about No-reference weighting factor selection for bimodal tomography
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views