- Read more about REAL-TIME DATA SELECTION AND ORDERING FOR COGNITIVE BIAS MITIGATION
- Log in to post comments
Abstract
We consider the problem of selecting and ordering a subset of N' out of N observations to be presented to a human being in the context of a binary hypothesis testing problem. We restrict our attention to i.i.d. Gaussian observations. We propose an extension of the approximate subset sum algorithm,and show that it can be used to solve the problem with polynomial complexity. Furthermore, we show that the solution yields near optimal detection performance when compared to the case where all N observations are optimally processed.
ICASSP_16.pdf
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views- Read more about Dirichlet process mixture models for time-dependent clustering
- Log in to post comments
In many problems of signal processing, an important task is the classification of data. A group of methods that has attracted much interest for this purpose are the nonparametric Bayesian methods, and in particular, those based on the Dirichlet process. A useful metaphor for various generalizations of the Dirichlet process has been the Chinese restaurant process. Often the task of classification must be carried out in a sequential manner, and to that end the concepts from Bayesian non-parametrics cannot be applied straightforwardly.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views- Read more about ON PARAMETER ESTIMATION OF SYMMETRIC ALPHA-STABLE DISTRIBUTION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views- Read more about Sequential Monte Carlo sampling for correlated latent long-memory time-series
- Log in to post comments
We propose sequential Monte Carlo (SMC) methods for state-space models. The latent processes represent correlated mixtures of fractional Gaussian processes embedded in white Gaussian noises and the observed data are nonlinear functions of the latent states.
- Categories:
 2 Views
2 Views- Read more about Detection of cyclostationarity in the presence of temporal or spatial structure with applications to cognitive radio
- Log in to post comments
Poster.pdf
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about STUDY OF ATTENUATION DUE TO WET ANTENNA IN MICROWAVE RADIO COMMUNICATION
- Log in to post comments
Atmospheric conditions are known to affect the Received Sig- nal Level (RSL) in commercial microwave links (MWLs), that operate at frequencies of tens of GHz. Study of these ef- fects is of great importance both for communication engineers and for environmental monitoring. In this paper we study the phenomenon of a wet antenna. During periods of high rela- tive humidity (RH), a thin layer of water may collect on the outside cover of the microwave units, resulting in increased signal attenuation. Here, we focus on the estimation of the signal power loss caused due to this phenomenon.
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
- Read more about Sequential Bayesian Algorithms for Identification and Blind Equalization of Unit-Norm Channels
- Log in to post comments
In many estimation problems of interest the unknown parameters reside on spherical manifolds. As most common filtering algorithms assume that parameters have Gaussian prior distributions, their application to such problems leads to suboptimal performance. In this letter, we propose a model in which the unknown unit-norm parameter vectors have Fisher-Bingham (F-B) prior distributions.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views- Read more about Oligopoly Dynamic Pricing: A Repeated Game with Incomplete Information
- Log in to post comments
We consider an oligopoly dynamic pricing problem where the demand model is unknown and the sellers have different marginal costs. We formulate the problem as a repeated game with incomplete information. We develop a dynamic pricing strategy that leads to a Pareto-efficient and subgame-perfect equilibrium and offers a bounded regret over an infinite horizon, where regret is defined as the expected cumulative profit loss as compared to the ideal scenario with a known demand model.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views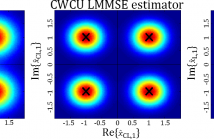
- Read more about Component-Wise Conditionally Unbiased Widely Linear MMSE Estimation
- Log in to post comments
Biased estimators can outperform unbiased ones in terms of the mean square error (MSE). In this work we treat all estimators in the Bayesian framework, where the best linear unbiased estimator (BLUE) fulfills the so called global conditional unbiased constraint. Recently, component-wise conditionally unbiased linear minimum mean square error (CWCU LMMSE) estimators have been introduced.
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views- Read more about On the Particle-Assisted Stochastic Search in Cooperative Wireless Network Localization
- Log in to post comments
Cooperative localization plays a key role in location aware service of wireless networks. However, the statistical-based estimator of network localization, e.g., the maximum likelihood estimator (MLE) or the maximum a posterior (MAP) estimator, is commonly non-convex due to the nonlinear measurement function and/or the non-Gaussian disturbance, which complicates the localization of network nodes. In this paper, a novel particleassisted
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views