- Read more about Frequency Estimation for a Mixture of Sinusoids: A Near-Optimal Sequential Approach
- Log in to post comments
An extended version of the paper has been submitted to IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing (TSP):
B. Mamandipoor, D. Ramasamy, U. Madhow, “Newtonized Orthogonal Matching Pursuit: Frequency Estimation over the Continuum,”arXiv preprint arXiv:1509.01942, 2015.
A MATLAB implementation of the algorithm can be found here:
https://bitbucket.org/wcslspectralestimation/continuous-frequency-estima...
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 ViewsThis paper considers the detection of possible deviation from a nominal distribution for continuously valued random variables. Specifically, under the null hypothesis, samples are distributed approximately according to a nominal distribution. Any significant departure from this nominal distribution constitutes the alternative hypothesis. It is established that for such deviation detection where the nominal distribution is only specified under the null hypothesis, Kullback-Leibler distance is not a suitable measure for deviation.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views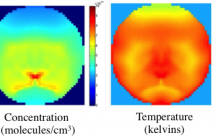
- Read more about Gaussian Mixture Prior Models for Imaging of Flow Cross Sections from Sparse Hyperspectral Measurements
- Log in to post comments
This is an overview presentation about developing accurate prior models that can capture non-Gaussian characteristics of images. The slides use tunable diode laser absorption tomography (TDLAT) as an application to show the results.
For more information, please check out the publication at IEEE Xplore:
Zeeshan Nadir, Michael S. Brown, Mary L. Comer, Charles A. Bouman, “Gaussian Mixture Prior Models for Imaging of Flow Cross Sections from Sparse Hyperspectral Measurements” , 2015 IEEE GlobalSIP Conference, Dec 14-16
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views- Read more about Joint Composite Detection and Bayesian Estimation: A Neyman-Pearson Approach
- Log in to post comments
The paper considers the composite detection problem where both detection and parameter estimation are of primary interest. Based on a Neyman-Pearson type of formulation, our goal is to find the joint detector and estimator that minimizes a decision-dependent Bayesian estimation risk subject to the detection error probability constraints. The optimal joint solution not only yields lower Bayesian estimation risk compared to the conventional method, which combines the likelihood ratio test and the Bayesian estimator in sequence, but
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views- Read more about Multi-Sensor Generalized Sequential Probability Ratio Test Using Level-Triggered Sampling
- Log in to post comments
This paper investigates the generalized sequential probability ratio test (GSPRT) with multiple sensors. Focusing on the communication-constrained scenario, where sensors transmit one-bit messages to the fusion center, we propose a decentralized GSRPT based on level-triggered sampling scheme (LTS-GSPRT). The proposed LTS-GSPRT amounts to the algorithm where each sensor successively reports the decisions of local GSPRTs to the fusion center.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views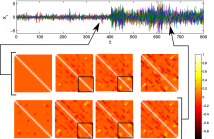
- Read more about Estimating Multi-Resolution Dependency Graphs within a Locally Stationary Wavelet Framework
- Log in to post comments
Estimation of sparse partial correlation graphs is discussed within the multivariate locally-stationary wavelet framework. We discuss the requirement for regularisation in such a framework and how this effects estimation. We observe that sparse model selection in the framework promotes more robust estimates of multivariate LSW processes, and improves interpretation through graph selection. The method is applied to study evolving correlation dynamics throughout an epileptic seizure.
globalSIP.pdf
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views- Read more about Sketching for Sequential Change-Point Detection
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views- Read more about Better than l0 Recovery via Blind Identification
- Log in to post comments
In this work, we propose a novel approach to multiple measurement vector (MMV) compressed sensing. We show that by exploiting the statistical properties of the sources, we can do better than previously derived lower bounds in this context. We show that in the MMV case, we can identify the active sources with fewer sensors than sources. We first develop a general framework for recovering the sparsity profile of the sources by combining ideas from compressed sensing with blind identification methods.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views- Read more about On the Particle-Assisted Stochastic Search In Cooperative Wireless Network Localization
- Log in to post comments
Cooperative localization plays a key role in location-aware service of wireless networks. However, the statistical-based estimator of network localization, e.g., the maximum likelihood estimator or the maximum a posterior estimator, is commonly non-convex due to nonlinear measurement function and/or non-Gaussian system disturbance, which complicates the localization of network nodes. In this presentation, a novel particle-assisted stochastic search (PASS) algorithm is proposed to find out the optimal node locations based on its non-convex objective function.
- Categories:
 2 Views
2 Views