- Read more about AMOS: An Automated Model Order Selection Algorithm for Spectral Graph Clustering
- Log in to post comments
One of the longstanding problems in spectral graph clustering (SGC) is the so-called model order selection problem: automated selection of the correct number of clusters. This is equivalent to the problem of finding the number of connected components or communities in an undirected graph. In this paper, we propose AMOS, an automated model order selection algorithm for SGC.
- Categories:
 113 Views
113 Views- Read more about Constrained Perturbation Regularization Approach for Signal Estimation Using Random Matrix Theory
- Log in to post comments
In this work, we propose a new regularization approach for linear least-squares problems with random matrices. In
the proposed constrained perturbation regularization approach, an artificial perturbation matrix with a bounded norm is forced
into the system model matrix. This perturbation is introduced to improve the singular-value structure of the model matrix and,
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
The ability to obtain accurate estimators from a set of measurements is a key factor in science and engineering. Typically, there is an inherent assumption that the measurements were taken in a sequential order, be it in space or time. However, data is increasingly irregular so this assumption of sequentially obtained measurements no longer holds. By leveraging notions of graph signal processing to account for these irregular domains, we propose an unbiased estimator for the mean of a wide sense stationary graph process based on the diffusion of a single realization.
- Categories:
 98 Views
98 Views- Read more about Estimation accuracy of non-standard maximum likelihood estimators
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views- Read more about Generalized Barankin-Type Lower Bounds for Misspecified Models
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views- Read more about Wirtinger Flow Method with Optimal Stepsize for Phase Retrieval
- Log in to post comments
The recently reported Wirtinger flow (WF) algorithm has been demonstrated as a promising method for solving the problem of phase retrieval by applying a gradient descent scheme. An empirical choice of stepsize is suggested in practice. However, this heuristic stepsize selection rule is not optimal. In order to accelerate the convergence rate, we propose an improved WF with optimal stepsize. It is revealed that this optimal stepsize is the solution of a univariate cubic equation with real-valued coefficients.
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views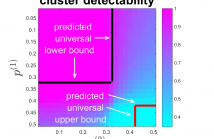
- Read more about Multilayer Spectral Graph Clustering via Convex Layer Aggregation
- Log in to post comments
Multilayer graphs are commonly used for representing different relations between entities and handling heterogeneous data processing tasks. New challenges arise in multilayer graph clustering for assigning clusters to a common multilayer node set and for combining information from each layer. This paper presents a theoretical framework for multilayer spectral graph clustering of the nodes via convex layer aggregation.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about Robust Regularized Least-Squares Beamforming Approach to Signal Estimation
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we address the problem of robust adaptive beamforming of signals received by a linear array. The challenge associated with the beamforming problem is twofold. Firstly, the process requires the inversion of the usually ill-conditioned covariance matrix of the received signals. Secondly, the steering vector pertaining to the direction of arrival of the signal of interest is not known precisely. To tackle these two challenges, the standard capon beamformer is manipulated to a form where the beamformer output is obtained as a scaled version of the inner product of two vectors.
MVDR-COPRA.pdf
- Categories:
 Views
Views