ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.


- Read more about Small Perturbation Analysis of Network Topologies
- Log in to post comments
ICASSP2018.pdf
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views
- Read more about An algorithm for multi subject fMRI analysis based on the SVD and penalized rank-1 matrix approximation
- Log in to post comments
In recent years, data driven methods have been successfully used for analyzing multi-subject functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) datasets. These methods attempt to learn shared spatial activation maps (SM) or voxel time courses (TC) from temporally or spatially concatenated fMRI datasets respectively. Most of the methods proposed so far do not distinguish whether a particular SM/TC is a group level component or only present in a certain subject dataset.
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views
- Read more about Dictionary learning algorithm for Multi-Subject fMRI analysis via temporal and spatial concatenation
- Log in to post comments
In recent history, dictionary learning (DL) methods have been successfully used for analyzing multi-subject functional magnetic resonance imaging. These algorithms try to learn group-level spatial activation maps (SM) or voxel time courses (TC) from temporally or spatially concatenated fMRI datasets respectively. However, in multi-subject fMRI studies, we are interested in both group-level TCs as well as SMs.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about Language Transfer of Audio Word2Vec: Learning Audio Segment Representations without Target Language Data
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views
- Read more about Stochastic Dynamical Systems Based Latent Structure Discovery in High-dimensional Time Series
- Log in to post comments
The brain encodes information by neural spiking activities, which can be described by time series data as spike counts. Latent Vari- able Models (LVMs) are widely used to study the unknown factors (i.e. the latent states) that are dependent in a network structure to modulate neural spiking activities. Yet, challenges in performing experiments to record on neuronal level commonly results in rela- tively short and noisy spike count data, which is insufficient to de- rive latent network structure by existing LVMs. Specifically, it is difficult to set the number of latent states.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about Domain independent key term extraction from spoken content based on context and term location information in the utterances
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about Generative Adversarial Network and its Applications to Speech Signal and Natural Language Processing
- Log in to post comments
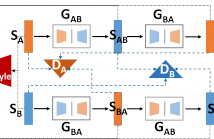
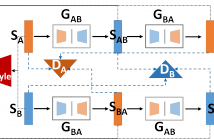
Generative adversarial network (GAN) is a new idea for training models, in which a generator and a discriminator compete against each other to improve the generation quality. Recently, GAN has shown amazing results in image generation, and a large amount and a wide variety of new ideas, techniques, and applications have been developed based on it. Although there are only few successful cases, GAN has great potential to be applied to text and speech generations to overcome limitations in the conventional methods.
- Categories:
 1621 Views
1621 Views