- Read more about Articulation GAN: Unsupervised Modeling of Articulatory Learning
- Log in to post comments
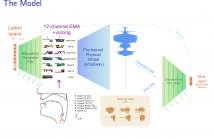
Generative deep neural networks are widely used for speech synthesis, but most existing models directly generate waveforms or spectral outputs. Humans, however, produce speech by controlling articulators, which results in the production of speech sounds through physical properties of sound propagation. We introduce the Articulatory Generator to the Generative Adversarial Network paradigm, a new unsupervised generative model of speech production/synthesis.
- Categories:
 81 Views
81 Views
- Read more about The Secret Source : Incorporating Source Features to Improve Acoustic-To-Articulatory Speech Inversion
- Log in to post comments
In this work, we incorporated acoustically derived source features, aperiodicity, periodicity and pitch as additional targets to an acoustic-to-articulatory speech inversion (SI) system. We also propose a Temporal Convolution based SI system, which uses auditory spectrograms as the input speech representation, to learn long-range dependencies and complex interactions between the source and vocal tract, to improve the SI task.
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views
- Read more about AN ERROR CORRECTION SCHEME FOR IMPROVED AIR-TISSUE BOUNDARY IN REAL-TIME MRI VIDEO FOR SPEECH PRODUCTION
- Log in to post comments
The best performance in Air-tissue boundary (ATB) segmentation of real-time Magnetic Resonance Imaging (rtMRI) videos in speech production is known to be achieved by a 3-dimensional convolutional neural network (3D-CNN) model. However, the evaluation of this model, as well as other ATB segmentation techniques reported in the literature, is done using Dynamic Time Warping (DTW) distance between the entire original and predicted contours. Such an evaluation measure may not capture local errors in the predicted contour.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about Multimodal Depression Classification Using Articulatory Coordination Features and Hierarchical Attention Based Text Embeddings
- Log in to post comments
Multimodal depression classification has gained immense popularity over the recent years. We develop a multimodal depression classification system using articulatory coordination features extracted from vocal tract variables and text transcriptions obtained from an automatic speech recognition tool that yields improvements of area under the receiver operating characteristics curve compared to unimodal classifiers (7.5% and 13.7% for audio and text respectively).
3649_poster.pdf
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views
- Read more about Acoustic comparison of physical vocal tract models with hard and soft walls
- Log in to post comments
This study explored how the frequencies and bandwidths of the acoustic resonances of physical tube models of the vocal tract differ when they have hard versus soft walls. For each of 10 tube shapes representing different vowels, two physical models were made: one with rigid plastic walls, and one with soft silicone walls. For all models, the acoustic transfer functions were measured and the bandwidths and frequencies of the first three resonances were determined.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF ESTIMATING ARTICULATORY MOVEMENTS FROM PHONEME SEQUENCES AND ACOUSTIC FEATURES
- Log in to post comments
Unlike phoneme sequences, movements of speech articulators (lips, tongue, jaw, velum) and the resultant acoustic signal are known to encode not only the linguistic message but also carry para-linguistic information. While several works exist for estimating articulatory movement from acoustic signals, little is known to what extent articulatory movements can be predicted only from linguistic information, i.e., phoneme sequence.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views
- Read more about SINGLE FREQUENCY FILTER BANK BASED LONG-TERM AVERAGE SPECTRA FOR HYPERNASALITY DETECTION AND ASSESSMENT IN CLEFT LIP AND PALATE SPEECH
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 43 Views
43 Views
- Read more about AN IMPROVED AIR TISSUE BOUNDARY SEGMENTATION TECHNIQUE FOR REAL TIME MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING VIDEO USING SEGNET
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents an improved methodology for the segmentation of the Air-Tissue boundaries (ATBs) in the upper airway of the human vocal tract using Real-Time Magnetic Resonance Imaging (rtMRI) videos. Semantic segmentation is deployed in the proposed approach using a Deep learning architecture called SegNet. The network processes an input image to produce a binary output image of the same dimensions having classified each pixel as air cavity or tissue, following which contours are predicted. A Multi-dimensional least square smoothing technique is applied to smoothen the contours.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views
- Read more about AIR-TISSUE BOUNDARY SEGMENTATION IN REAL TIME MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING VIDEO USING A CONVOLUTIONAL ENCODER-DECODER NETWORK
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a convolutional encoder-decoder network (CEDN) based approach for upper and lower Air-Tissue Boundary (ATB) segmentation within vocal tract in real-time magnetic resonance imaging (rtMRI) video frames. The output images from CEDN are processed using perimeter and moving average filters to generate smooth contours representing ATBs. Experiments are performed in both seen subject and unseen subject conditions to examine the generalizability of the CEDN based approach.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Representation learning using convolution neural network for acoustic-to-articulatory inversion
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 56 Views
56 Views