
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about Adversarial Teacher-Student Learning for Unsupervised Adaptation
- Log in to post comments
The teacher-student (T/S) learning has been shown effective in unsupervised domain adaptation ts_adapt. It is a form of transfer learning, not in terms of the transfer of recognition decisions, but the knowledge of posteriori probabilities in the source domain as evaluated by the teacher model. It learns to handle the speaker and environment variability inherent in and restricted to the speech signal in the target domain without proactively addressing the robustness to other likely conditions. Performance degradation may thus ensue.
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Vectorwise coordinate descent algorithm for spatially regularized independent low-rank matrix analysis
- Log in to post comments
Audio source separation is an important problem for many audio applications. Independent low-rank matrix analysis (ILRMA) is a recently proposed algorithm that employs the statistical independence between sources and the low-rankness of the time-frequency structure in each source. As reported in this paper, we have developed a new framework that enables us to introduce a spatial regularization of the demixing matrix in ILRMA.
- Categories:
 60 Views
60 Views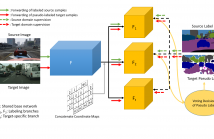
- Read more about A Fully Convolutional Tri-branch Network (FCTN) For Domain Adaptation
- Log in to post comments
A domain adaptation method for urban scene segmentation is proposed in this work. We develop a fully convolutional tri-branch network, where two branches assign pseudo labels to images in the unlabeled target domain while the third branch is trained with supervision based on images in the pseudo-labeled target domain. The re-labeling and re-training processes alternate. With this design, the tri-branch network learns target-specific discriminative representations progressively and, as a result, the cross-domain capability of the segmenter improves.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about Maximum-A-Posteriori Signal Recovery with Prior Information: Applications to Compressive Sensing
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
Traditional NMF-based signal decomposition relies on the factorization of spectral data, which is typically computed by means of short-time frequency transform. In this paper we propose to relax the choice of a pre-fixed transform and learn a short-time orthogonal transform together with the factorization. To this end, we formulate a regularized optimization problem reminiscent of conventional NMF, yet with the transform as additional unknown parameters, and design a novel block-descent algorithm enabling to find stationary points of this objective function.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about Streaming Influence Maximization in Social Networks based on Multi-Action Credit Distribution
- Log in to post comments
In a social network, influence maximization is the problem of identifying a set of users that own the maximum influence ability across the network. In this paper, a novel credit distribution (CD) based model, termed as the multi-action CD (mCD) model, is introduced to quantify the influence ability of each user. Compared to existing models, the new model can work with practical datasets where one type of action is recorded for multiple times. Based on this model, influence maximization is formulated as a submodular maximization problem under a knapsack constraint, which is NP-hard.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about Optimal Online Cyberbullying Detection
- Log in to post comments
Cyberbullying has emerged as a serious societal and public health problem that demands accurate methods for the detection of cyberbullying instances in an effort to mitigate the consequences. While techniques to automatically detect cyberbullying incidents have been developed, the scalability and timeliness of existing cyberbullying detection approaches have largely been ignored. We address this gap by formulating cyberbullying detection as a sequential hypothesis testing problem. Based on this formulation, we propose a novel
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views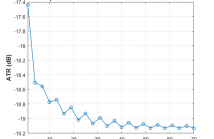
- Read more about Improved Noise Characterization for Relative Impulse Response Estimation
- Log in to post comments
Relative Impulse Responses (ReIRs) have several applications in speech enhancement, noise suppression and source localization for multi-channel speech processing in reverberant environments. Noise is usually assumed to be white Gaussian during the estimation of the ReIR between two microphones. We show that the noise in this system identification problem is instead dependent upon the microphone measurements and the ReIR itself.
ICASSP_V3.pdf
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
Performance-cost trade-offs in video object tracking tasks for long video sequences is investigated. A novel frame-subsampled, drift-resilient (FSDR) video object tracking algorithm is presented that would achieve desired tracking accuracy while dramatically reducing computing time by processing only sub-sampled video frames. A new pattern matching score metric is proposed to estimate the probability of drifting. A drift-recovery procedure is developed to enable the algorithm to recover from a drift situation and resume accurate tracking.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views