
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

In this paper, we propose a domain adversarial training (DAT) algorithm to alleviate the accented speech recognition problem. In order to reduce the mismatch between labeled source domain data (“standard” accent) and unlabeled target domain data (with heavy accents), we augment the learning objective for a Kaldi TDNN network with a domain adversarial training (DAT) objective to encourage the model to learn accent-invariant features.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views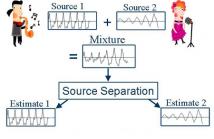
- Read more about Geometric Information Based Monaural Speech Separation Using Deep Neural Network
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 87 Views
87 Views
- Read more about RECOVERING SIGNALS FROM THEIR FROG TRACE
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Read more about STATISTICAL LEARNING OF RATIONAL WAVELET TRANSFORM FOR NATURAL IMAGES
- Log in to post comments
Motivated with the concept of transform learning and the utility of rational wavelet transform in audio and speech processing, this paper proposes Rational Wavelet Transform Learning in Statistical sense (RWLS) for natural images. The proposed RWLS design is carried out via lifting framework and is shown to have a closed form solution. The efficacy of the learned transform is demonstrated in the application of compressed sensing (CS) based reconstruction. The learned RWLS is observed to perform better than the existing standard dyadic wavelet transforms.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views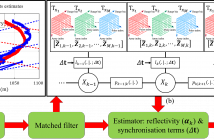
- Read more about OPPORTUNISTIC SYNCHRONISATION OF MULTI-STATIC STARING ARRAY RADARS VIA TRACK-BEFORE-DETECT
- Log in to post comments
In this work, we consider the problem of synchronising separately located transmitters and a staring array receiver that also has a local transmitter. The acknowledged benefits of using separate transmitters in active sensing are often undermined by the difficulty in accurate synchronisation of the receiver and the transmitters. In this work, we propose a solution that is based on measurements from non-cooperative objects in the illuminated region. We formulate the problem as parameter estimation in a state space model with individual transmitter channel data cubes as measurements.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views
Self-reset analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) allow for digitization of a signal with a high dynamic range. The reset action is equivalent to a modulo operation performed on the signal. We consider the problem of recovering the original signal from the measured modulo-operated signal. In our formulation, we assume that the underlying signal is Lipschitz continuous. The modulo-operated signal can be expressed as the sum of the original signal and a piecewise-constant signal that captures the transitions. The reconstruction requires estimating the piecewise-constant signal.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
Self-reset analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) allow for digitization of a signal with a high dynamic range. The reset action is equivalent to a modulo operation performed on the signal. We consider the problem of recovering the original signal from the measured modulo-operated signal. In our formulation, we assume that the underlying signal is Lipschitz continuous. The modulo-operated signal can be expressed as the sum of the original signal and a piecewise-constant signal that captures the transitions. The reconstruction requires estimating the piecewise-constant signal.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views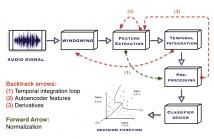
- Read more about Extended Pipeline for Content-Based Feature Engineering in Music Genre Recognition
- Log in to post comments
We present a feature engineering pipeline for the construction of musical signal characteristics, to be used for the design of a supervised model for musical genre identification. The key idea is to extend the traditional two-step process of extraction and classification with additive stand-alone phases which are no longer organized in a waterfall scheme. The whole system is realized by traversing backtrack arrows and cycles between various stages.
- Categories:
 45 Views
45 Views
- Read more about PREDICTING TONGUE MOTION IN UNLABELED ULTRASOUND VIDEO USING 3D CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
A 3-dimensional convolutional neural network is trained on unlabeled ultrasound video to predict an upcoming tongue image from previous ones. The network obtains results superior to those of simpler predictors, and provides a starting point for exploiting the higher-level representation of the tongue learned by the system in a variety of applications in speech research. This work is believed to be the first application of convolutional neural networks to unlabeled ultrasound video for the purpose of predicting tongue movement.
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views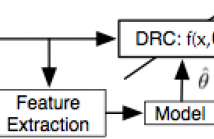
- Read more about FEATURE DESIGN USING AUDIO DECOMPOSITION FOR INTELLIGENT CONTROL OF THE DYNAMIC RANGE COMPRESSOR
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes a method of controlling the dynamic range compressor using sound examples. Our earlier work showed the effectiveness of random forest regression to map acoustic features to effect control parameters. We extend this work to address the challenging task of extracting relevant features when audio events overlap. We assess differ- ent audio decomposition approaches such as onset event detection, NMF, and transient/stationary audio separation using ISTA and compare feature extraction strategies for each case.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views