
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about Slides: Change-Point Detection of Gaussian Graph Signals with Partial Information
- Log in to post comments
slides.pdf
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
- Read more about UNEQUAL ERROR PROTECTION QUERYING POLICIES FOR THE NOISY 20 QUESTIONS PROBLEM
- Log in to post comments
We propose a non-adaptive unequal error protection (UEP) querying policy based on superposition coding for the noisy 20 questions problem.
In this problem, a player wishes to successively refine an estimate of the value of a continuous random variable by posing binary queries and receiving noisy responses.
When the queries are designed non-adaptively as a single block and the noisy responses are modeled as the outputs of a binary symmetric channel the 20 questions problem can be mapped to an equivalent problem of channel coding with UEP.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 ViewsIn query expansion for object retrieval, there is substantial danger of query drift, where irrelevant information is inferred from pseudo-relevant images to enrich the query. To address this issue, we propose a query expansion method from the viewpoint of diffusion. It explores the structure of highly ranked images in a topological space, assuming that false positives reside on different manifolds from the query. For this purpose, a mutual rank graph is defined on pseudo-relevant images, and their distribution is learned by diffusing their query similarities through the graph.
ICASSP18.2.pdf
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about AN EFFICIENT TARGET LOCALIZATION ESTIMATOR FROM BISTATIC RANGE AND TDOA MEASUREMENTS IN MULTISTATIC RADAR
- Log in to post comments
This paper considers the target localization problem using the hybrid bistatic range and time difference of arrival (TDOA) measurements in multistatic radar. An algebraic closed-form solution to this nonlinear estimation problem is developed through two-stage processing, where the nuisance variables are introduced in the first stage and the localization error of first stage solution is estimated to improve the final target position estimate in the second stage.
- Categories:
 57 Views
57 Views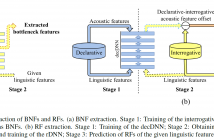
Speaking style plays an important role in the expressivity of speech for communication. Hence speaking style is very important for synthetic speech as well. Speaking style adaptation faces the difficulty that the data of specific styles may be limited and difficult to obtain in large amounts. A possible solution is to leverage data from speaking styles that are more available, to train the speech synthesizer and then adapt it to the target style for which the data is scarce.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views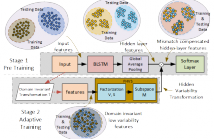
- Read more about FACTORIZED HIDDEN VARIABILITY LEARNING FOR ADAPTATION OF SHORT DURATION LANGUAGE IDENTIFICATION MODELS
- Log in to post comments
Bidirectional long short term memory (BLSTM) recurrent neural networks (RNNs) have recently outperformed other state-of-the-art approaches, such as i-vector and deep neural networks (DNNs) in automatic language identification (LID), particularly when testing with very short utterances (∼3s). Mismatches conditions between training and test data, e.g. speaker, channel, duration and environmental noise, are a major source of performance degradation for LID.
POSTER.pdf
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about AUTOMATIC BIRD VOCALIZATION IDENTIFICATION BASED ON FUSION OF SPECTRAL PATTERN AND TEXTURE FEATURES
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about SIMULTANEOUS ACCURATE DETECTION OF PULMONARY NODULES AND FALSE POSITIVE REDUCTION USING 3D CNNS
- Log in to post comments
ICASSP_qyl.pdf
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about Source-Aware Context Network for Single-Channel Multi-speaker Speech Separation
- Log in to post comments
Deep learning based approaches have achieved promising performance in speaker-dependent single-channel multi-speaker speech separation.However, partly due to the label permutation problem, they may encounter difficulties in speaker-independent conditions. Recent methods address this problem by some assignment operations. Different from them, we propose a novel source-aware context network, which explicitly inputs speech sources as well as mixture signal.
version2.pdf
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views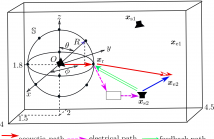
- Read more about Reference Signal Generation for Broadband ANC Systems in Reverberant Rooms
- Log in to post comments
One major issue of implementing broadband active noise control systems in reverberant
rooms is the lack of reference signals. In this work, by exploiting the spatial sound
field characteristics, a time-domain sound field separation method is developed to
generate the reference signal for broadband active noise control systems in reverberant
rooms. The time-domain sound field separation method separates the outgoing field produced
by the primary source from the secondary source feedback and room reverberation on a
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views