
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

In recent years, the successful application of Deep Learning methods to classification problems has had a huge impact in many domains. In biomedical engineering, the problem of gesture recognition based on electromyography is often addressed as an image classification problem using Convolutional Neural Networks. In this paper, we approach
- Categories:
 66 Views
66 Views
- Read more about Fully Supervised Speaker Diarization
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a fully supervised speaker diarization approach, named unbounded interleaved-state recurrent neural networks (UIS-RNN). Given extracted speaker-discriminative embeddings (a.k.a. d-vectors) from input utterances, each individual speaker is modeled by a parameter-sharing RNN, while the RNN states for different speakers interleave in the time domain. This RNN is naturally integrated with a distance-dependent Chinese restaurant process (ddCRP) to accommodate an unknown number of speakers.
- Categories:
 107 Views
107 Views
- Read more about Tuplemax Loss for Language Identification
- Log in to post comments
In many scenarios of a language identification task, the user will specify a small set of languages which he/she can speak instead of a large set of all possible languages. We want to model such prior knowledge into the way we train our neural networks, by replacing the commonly used softmax loss function with a novel loss function named tuplemax loss. As a matter of fact, a typical language identification system launched in North America has about 95% users who could speak no more than two languages.
- Categories:
 48 Views
48 Views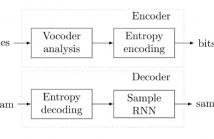
- Read more about HIGH-QUALITY SPEECH CODING WITH SAMPLE RNN
- Log in to post comments
We provide a speech coding scheme employing a generative model based on SampleRNN that, while operating at significantly lower bitrates, matches or surpasses the perceptual quality of state-of-the-art classic wide-band codecs. Moreover, it is demonstrated that the proposed scheme can provide a meaningful rate-distortion trade-off without retraining. We evaluate the proposed scheme in a series of listening tests and discuss limitations of the approach.
- Categories:
 371 Views
371 Views
- Read more about LINEAR PREDICTION-BASED PART-DEFINED AUTO-ENCODER USED FOR SPEECH ENHANCEMENT
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes a linear prediction-based part-defined auto-encoder (PAE) network to enhance speech signal. The PAE is a defined decoder or an established encoder network, based on an efficient learning algorithm or classical model. In this paper, the PAE utilizes AR-Wiener filter as the decoder part, and the AR-Wiener filter is modified as a linear prediction (LP) model by incorporating the modified factor from the residual signal. The parameters of line spectral frequency (LSF) of speech and noise and the Wiener filtering mask are utilized for training targets.
- Categories:
 90 Views
90 Views
- Read more about Dynamic Point Cloud Geometry Compression via Patch-wise Polynomial Fitting
- Log in to post comments
With the boosting requirements of realistic 3D modeling for immersive applications, advent of the newly-developed 3D point cloud has attracted great attention. Frankly, immersive experience using high data volume affirms the importance of efficient compression. Inspired by the video-based point cloud compression (V-PCC), we propose a novel point cloud compression algorithm based on polynomial fitting of proper patches. Moreover, the original point cloud is segmented into various patches.
- Categories:
 90 Views
90 Views
We present a novel event embedding algorithm for crime data that can jointly capture time, location, and the complex free-text component of each event. The embedding is achieved by regularized Restricted Boltzmann Machines (RBMs), and we introduce a new way to regularize by imposing a ℓ1 penalty on the conditional distributions of the observed variables of RBMs. This choice of regularization performs feature selection and it also leads to efficient computation since the gradient can be computed in a closed form.
- Categories:
 91 Views
91 Views
- Read more about Poster of 'DEEP HYBRID NETWORKS BASED RESPONSE SELECTION FOR MULTI-TURN DIALOGUE SYSTEMS'
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 90 Views
90 Views
- Read more about GRAPH-BASED RGB-D IMAGE SEGMENTATION USING COLOR-DIRECTIONAL-REGION MERGING
- Log in to post comments
Color and depth information provided simultaneously in RGB-D images can be used to segment scenes into disjoint regions. In this paper, a graph-based segmentation method for RGB-D image is proposed, in which an adaptive data-driven combination of color- and normal-variation is presented to construct dissimilarity between two adjacent pixels and a novel region merging threshold exploiting normal information in adjacent regions is proposed to control the proceeding of the region merging.
- Categories:
 104 Views
104 Views
- Read more about USING DEEP-Q NETWORK TO SELECT CANDIDATES FROM N-BEST SPEECH RECOGNITION HYPOTHESES FOR ENHANCING DIALOGUE STATE TRACKING
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 82 Views
82 Views