
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

360 camera has recently become popular since it can capture the whole 360 scene. A large number of related applications have been springing up. In this paper, We propose a deep learning based object detector that can be applied directly on 360 images. The proposed detector is based on modifications of the faster RCNN model. Three modification schemes are proposed here, including (1) distortion data augmentation, (2) introducing muilti-kernel layers for improving accuracy for distorted object detection, and (3) adding position information into the model for learning spatial information.
ICASSP_poster300.pdf
- Categories:
 113 Views
113 Views
- Read more about Low-latency deep clustering for speech separation
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes a low algorithmic latency adaptation of the deep clustering approach to speaker-independent speech separation. It consists of three parts: a) the usage of long-short-term-memory (LSTM) networks instead of their bidirectional variant used in the original work, b) using a short synthesis window (here 8 ms) required for low-latency operation, and, c) using a buffer in the beginning of audio mixture to estimate cluster centres corresponding to constituent speakers which are then utilized to separate speakers within the rest of the signal.
- Categories:
 81 Views
81 Views
- Read more about Representation learning using convolution neural network for acoustic-to-articulatory inversion
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 56 Views
56 Views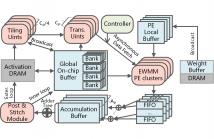
- Read more about A Low-latency Sparse-winograd Accelerator for Convolutional Neural Networks
- Log in to post comments
Poster.pdf
- Categories:
 84 Views
84 Views
- Read more about DISTRIBUTED JOINT TRANSMITTER DESIGN AND SELECTION USING AUGMENTED ADMM
- Log in to post comments
This work considers a design of network in which multiple transmission points (TPs) cooperatively serve users by jointly precoding shared data. Considered problem formulation jointly designs the beamformers and performs TP-UE link selection, which aims in improving overall system rate. Proposed distributed Augmented ADMM algorithm features parallelization among TPs, which has practical importance for computational load distribution and reducing signaling overhead in backhaul.
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views
- Read more about DISTRIBUTED JOINT TRANSMITTER DESIGN AND SELECTION USING AUGMENTED ADMM
- Log in to post comments
This work considers a design of network in which multiple transmission points (TPs) cooperatively serve users by jointly precoding shared data. Considered problem formulation jointly designs the beamformers and performs TP-UE link selection, which aims in improving overall system rate. Proposed distributed Augmented ADMM algorithm features parallelization among TPs, which has practical importance for computational load distribution and reducing signaling overhead in backhaul. This approach is different from others
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views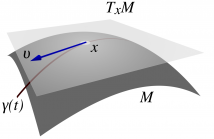
- Read more about Nonlinear State Estimation using Particle Filters on the Stiefel Manifold
- Log in to post comments
Many problems in statistical signal processing involve tracking the state of a dynamic system that evolves on a Stiefel manifold. To this aim, we introduce in this paper a novel particle filter algorithm that approximates the optimal importance function on the Stiefel manifold and is capable of handling nonlinear observation functions. To sample from the required importance function, we develop adaptations of previous MCMC algorithms.
- Categories:
 86 Views
86 Views
- Read more about SPEECH ARTIFACT REMOVAL FROM EEG RECORDINGS OF SPOKEN WORD PRODUCTION WITH TENSOR DECOMPOSITION
- Log in to post comments
Research about brain activities involving spoken word production is considerably underdeveloped because of the undiscovered characteristics of speech artifacts, which contaminate electroencephalogram (EEG) signals and prevent the inspection of the underlying cognitive processes. To fuel further EEG research with speech production, a method using three-mode tensor decomposition (time x space x frequency) is proposed to perform speech artifact removal. Tensor decomposition enables simultaneous inspection of multiple modes, which suits the multi-way nature of EEG data.
- Categories:
 223 Views
223 Views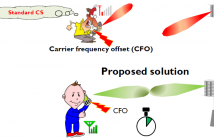
- Read more about [Poster] Localized Random Sampling for Robust Compressive Beam Alignment
- Log in to post comments
Compressed sensing (CS)-based beam alignment is a promising solution for rapid link configuration in millimeter wave (mmWave)
- Categories:
 84 Views
84 Views
- Read more about MASSIVE MIMO CHANNEL ESTIMATION FOR MILLIMETER WAVE SYSTEMS VIA MATRIX COMPLETION
- Log in to post comments
Millimeter wave (mmWave) massive multiple input multiple output (MIMO) systems realizing directive beamforming require reliable estimation of the wireless propagation channel. However, mmWave channels are characterized by high variability that severely challenges their recovery over short training periods. Current channel estimation techniques exploit either the channel sparsity in the beamspace domain or its low-rank property in the antenna domain, nevertheless, they still require large numbers of training symbols for the satisfactory performance.
- Categories:
 204 Views
204 Views