
- Read more about MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD-BASED GRIDLESS DOA ESTIMATION USING STRUCTURED COVARIANCE MATRIX RECOVERY AND SBL WITH GRID REFINEMENT
- Log in to post comments
We consider the parametric measurement model employed in applications such as line spectral or direction-of-arrival estimation with the goal to estimate the underlying parameter in a gridless manner. We focus on the stochastic maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) framework and overcome the model complexities of the past by reparameterization of the objective and exploiting the sparse Bayesian learning (SBL) approach. SBL is shown to be a correlation-aware method and, for the underlying problem, a grid-based technique for recovering a structured covariance matrix of the measurements.
- Categories:
 41 Views
41 Views
- Read more about Deep convolution network based super resolution DOA estimation with Toeplitz and sparse prior
- Log in to post comments
Slides
DCN_ESCM.pptx
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about Gridless Parameter Estimation in Partly Calibrated Rectangular Arrays
- Log in to post comments
Poster for the paper SAM-P6.7: GRIDLESS PARAMETER ESTIMATION IN PARTLY CALIBRATED RECTANGULAR ARRAYS in IEEE ICASSP 2024
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views
- Read more about Subspace-Based Co-Array Processing for Nested Arrays Without Eigendecomposition
- Log in to post comments
For the purpose of computational efficiency, we propose two subspace-based methods, but without eigendecomposition, to address the two typical problems in nested array processing, i.e., direction-of-arrival (DOA) estimation and noise elimination. In detail, to estimate DOA parameters, we judiciously arrange the segments extracted from the co-array model and then introduce a novel co-array-based orthogonal propagator method (COPM).
document.pdf
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views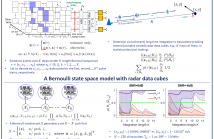
- Read more about Coherent long-time integration and Bayesian detection with Bernoulli track-before-detect
- Log in to post comments
We consider the problem of detecting small and manoeuvring objects with staring array radars. Coherent processing and long-time integration are key to addressing the undesirably low signal-to-noise/background conditions in this scenario and are complicated by the object manoeuvres. We propose a Bayesian solution that builds upon a Bernoulli state space model equipped with the likelihood of the radar data cubes through the radar ambiguity function. Likelihood evaluation in this model corresponds to coherent long-time integration.
- Categories:
 72 Views
72 Views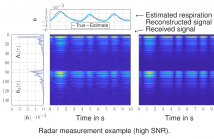
- Read more about Variational Message Passing-based Respiratory Motion Estimation and Detection Using Radar Signals
- Log in to post comments
We present a variational message passing (VMP)-based approach to detect the presence of a person based on their respiratory chest motion using multistatic ultra-wideband (UWB) radar. In the process, the respiratory motion is estimated for contact-free vital sign monitoring. The received signal is modeled as a backscatter channel and the respiratory motion and propagation channels are estimated using VMP. We use the evidence lower bound (ELBO) to approximate the model evidence for the detection.
- Categories:
 44 Views
44 Views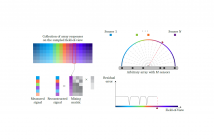
- Read more about EUSIPCO 2020 Tutorial: Four Decades of Array Signal Processing Research: An Optimization Relaxation Technique Perspective
- Log in to post comments
In our community, we currently witness that sensor array processing, more specifically direction-of- arrival (DoA) estimation, receives new momentum due to the emergence of new applications such as automotive radar, drone localization, parametric channel estimation in Massive MIMO. This development is further inspired by the emergence of new powerful and affordable multiantenna hardware platforms.
- Categories:
 160 Views
160 Views
- Read more about IEEE SAM 2022 Tutorial: Four Decades of Array Signal Processing Research: An Optimization Relaxation Technique Perspective
- Log in to post comments
In our community, we currently witness that sensor array processing, more specifically direction-of-arrival (DoA) estimation, receives new momentum due to the emergence of new applications such as automotive radar, drone localization, parametric channel estimation in Massive MIMO. This development is further inspired by the emergence of new powerful and affordable multiantenna hardware platforms.
- Categories:
 204 Views
204 Views
- Read more about Acquisition of Asynchronous Data and Parameter Estimation based on Double-Cross- Correlation Processor with Phase Transform (Demo at WASPAA 2021)
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Coherent processing of signals captured by a wireless acoustic sensor network (WASN) requires an estimation of such parameters as the sampling-rate and sampling-time offset (SRO and STO). The acquired asynchronous signals of such WASN exhibit an accumulating time drift (ATD) linearly growing with time and dependent on SRO and STO values. In our demonstration, we present a real WASN based on Respberry-Pi computers, where SRO and ATD values are estimated by using a double-cross-correlation processor with phase transfrom (DXCP-PhaT) recently proposed.
- Categories:
 173 Views
173 Views
- Read more about CRAMÉR-RAO BOUND AND ANTENNA SELECTION OPTIMIZATION FOR DUAL RADAR-COMMUNICATION DESIGN
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views