
- Read more about Network Adaptation Strategies for Learning New Classes without Forgetting the Original Ones
- Log in to post comments
We address the problem of adding new classes to an existing classifier without hurting the original classes, when no access is allowed to any sample from the original classes. This problem arises frequently since models are often shared without their training data, due to privacy and data ownership concerns. We propose an easy-to-use approach that modifies the original classifier by retraining a suitable subset of layers using a linearly-tuned, knowledge-distillation regularization.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about Peak Detection and Baseline Correction using a Convolution Neural Network
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 270 Views
270 Views
- Read more about Divergence Based Weighting for Information Channels in Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Bird Audio Detection
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we address the problem of bird audio detec-
tion and propose a new convolutional neural network archi-
tecture together with a divergence based information channel
weighing strategy in order to achieve improved state-of-the-
art performance and faster convergence. The effectiveness of
the methodology is shown on the Bird Audio Detection Chal-
lenge 2018 (Detection and Classification of Acoustic Scenes
and Events Challenge, Task 3) development data set.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about SPATIALLY ADAPTIVE LOSSES FOR VIDEO SUPER-RESOLUTION WITH GANS
- Log in to post comments
ICASSP_PPT.pdf
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about Stochatic Adaptive Neural Architecture Search
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about Improve Diverse Text Generation by Self Labeling Conditional Variational Auto Encoder
- Log in to post comments
Diversity plays a vital role in many text generating applications. In recent years, Conditional Variational Auto Encoders (CVAE) have shown promising performances for this task. However, they often encounter the so called KL-Vanishing problem. Previous works mitigated such problem by heuristic methods such as strengthening the encoder or weakening the decoder while optimizing the CVAE objective function. Nevertheless, the optimizing direction of these methods are implicit and it is hard to find an appropriate degree to which these methods should be applied.
slcvae.pptx
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
- Read more about An End-to-End Network to Synthesize Intonation using a Generalized Command Response Model - Poster
- Log in to post comments
The generalized command response (GCR) model represents intonation as a
superposition of muscle responses to spike command signals. We have previously
shown that the spikes can be predicted by a two-stage system, consisting of a recurrent neural network and a post-processing procedure, but the responses themselves were fixed dictionary atoms. We propose an end-to-end
neural architecture that replaces the dictionary atoms with trainable
second-order recurrent elements analogous to recursive filters. We demonstrate
- Categories:
 167 Views
167 Views
- Read more about 1-D Convolutional Neural Networks for Signal Processing Applications
- Log in to post comments
1D Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have recently become the state-of-the-art technique for crucial signal processing applications such as patient-specific ECG classification, structural health monitoring, anomaly detection in power electronics circuitry and motor-fault detection. This is an expected outcome as there are numerous advantages of using an adaptive and compact 1D CNN instead of a conventional (2D) deep counterparts.
- Categories:
 420 Views
420 Views
- Read more about DEEP LEARNING THE EEG MANIFOLD FOR PHONOLOGICAL CATEGORIZATION FROM ACTIVE THOUGHTS
- Log in to post comments
Speech-related Brain Computer Interfaces (BCI) aim primarily at finding an alternative vocal communication pathway for
people with speaking disabilities. As a step towards full decoding of imagined speech from active thoughts, we present a
BCI system for subject-independent classification of phonological categories exploiting a novel deep learning based
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views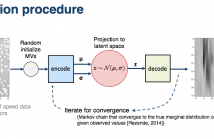
- Read more about Missing Data In Traffic Estimation: A Variational Autoencoder Imputation Method
- Log in to post comments
Road traffic forecasting systems are in scenarios where sensor or system failure occur. In those scenarios, it is known that missing values negatively affect estimation accuracy although it is being often underestimate in current deep neural network approaches. Our assumption is that traffic data can be generated from a latent space. Thus, we propose an online unsupervised data imputation method based on learning the data distribution using a variational autoencoder (VAE).
- Categories:
 208 Views
208 Views