
- Read more about Regression versus classification for neural network based audio source localization
- Log in to post comments
poster_v2.pdf
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about Self-supervised representation learning from electroencephalography signals
- Log in to post comments
The supervised learning paradigm is limited by the cost - and sometimes the impracticality - of data collection and labeling in multiple domains. Self-supervised learning, a paradigm which exploits the structure of unlabeled data to create learning problems that can be solved with standard supervised approaches, has shown great promise as a pretraining or feature learning approach in fields like computer vision and time series processing. In this work, we present self-supervision strategies that can be used to learn informative representations from multivariate time series.
- Categories:
 93 Views
93 Views
- Read more about Incorporating Intra-Spectral Dependencies With A Recurrent Output Layer For Improved Speech Enhancement
- Log in to post comments
Deep-learning based speech enhancement systems have offered tremendous gains, where the best performing approaches use long short-term memory (LSTM) recurrent neural networks (RNNs) to model temporal speech correlations. These models, however, do not consider the frequency-level correlations within a single time frame, as spectral dependencies along the frequency axis are often ignored. This results in inaccurate frequency responses that negatively affect perceptual quality and intelligibility. We propose a deep-learning approach that considers temporal and frequency-level dependencies.
- Categories:
 56 Views
56 Views
- Read more about Deep Learning for MRI Reconstruction Using a Novel Projection Based Cascaded Network
- Log in to post comments
After their triumph in various classification, recognition and segmentation problems, deep learning and convolutional networks are now making great strides in different inverse problems of imaging. Magnetic resonance image (MRI) reconstruction is an important imaging inverse problem, where deep learning methodologies are starting to make impact. In this work we will develop a new Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) based variant for MRI reconstruction. The developed algorithm is based on the recently proposed deep cascaded CNN (DC-CNN) structure.
- Categories:
 121 Views
121 Views
- Read more about Improving Neural Non-Maximum Suppression For Object Detection By Exploiting Interest-Point Detector
- Log in to post comments
Non-maximum suppression (NMS) is a post-processing step in almost every visual object detector. Its goal is to drastically prune the number of overlapping detected candidate regions-of-interest (ROIs) and replace them with a single, more spatially accurate detection. The default algorithm (Greedy NMS) is fairly simple and suffers from drawbacks, due to its need for manual tuning. Recently, NMS has been improved using deep neural networks that learn how to solve a spatial overlap-based detections rescoring task in a supervised manner, where only ROI coordinates are exploited as input.
- Categories:
 151 Views
151 Views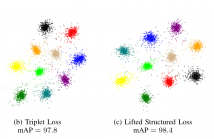
- Read more about Deep Metric Learning using Similarities from Nonlinear Rank Approximations
- Log in to post comments
In recent years, deep metric learning has achieved promising results in learning high dimensional semantic feature embeddings where the spatial relationships of the feature vectors match the visual similarities of the images. Similarity search for images is performed by determining the vectors with the smallest distances to a query vector. However, high retrieval quality does not depend on the actual distances of the feature vectors, but rather on the ranking order of the feature vectors from similar images.
- Categories:
 63 Views
63 Views
- Read more about Sinogram Image Completion for Limited Angle Tomography with Generative Adversarial Networks
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 50 Views
50 Views
- Read more about Shift R-CNN: Deep Monocular 3D Object Detection with Closed-Form Geometric Constraints
- Log in to post comments
We propose Shift R-CNN, a hybrid model for monocular 3D object detection, which combines deep learning with the power of geometry. We adapt a Faster R-CNN network for regressing initial 2D and 3D object properties and combine it with a least squares solution for the inverse 2D to 3D geometric mapping problem, using the camera projection matrix. The closed-form solution of the mathematical system, along with the initial output of the adapted Faster R-CNN are then passed through a final ShiftNet network that refines the result using our newly proposed Volume Displacement Loss.
- Categories:
 144 Views
144 Views
- Read more about CLOUDMASKGAN: A CONTENT-AWARE UNPAIRED IMAGE-TO-IMAGE TRANSLATION ALGORITHM FOR REMOTE SENSING IMAGERY
- Log in to post comments
Cloud segmentation is a vital task in applications that utilize satellite imagery. A common obstacle in using deep learning-based methods for this task is the insufficient number of images with their annotated ground truths. This work presents a content-aware unpaired image-to-image translation algorithm. It generates synthetic images with different land cover types from original images while preserving the locations and the intensity values of the cloud pixels. Therefore, no manual annotation of ground truth in these images is required.
- Categories:
 47 Views
47 Views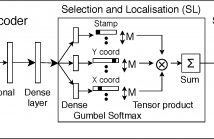
Unsupervised object discovery in images involves uncovering recurring patterns that define objects and discriminates them against the background. This is more challenging than image clustering as the size and the location of the objects are not known: this adds additional degrees of freedom and increases the problem complexity. In this work, we propose StampNet, a novel autoencoding neural network that localizes shapes (objects) over a simple background in images and categorizes them simultaneously.
StampNet.pdf
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views