
- Read more about MPEG-G Reference-Based Compression of Unaligned Reads Through Ultra-Fast Alignments
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
With the widespread application of next generation sequencing technologies, the volume of sequencing data became comparable to that of big data domains. The compression of sequencing reads (nucleotide sequences, quality values, read names), in both raw and aligned data, is a way to alleviate bandwidth, transfer, and storage requirements of genomics pipelines. ISO/IEC MPEG-G standardizes the compressed representation (i.e. storage and streaming) of structured, indexed sets of genomic sequencing data for both raw and aligned data.
- Categories:
 46 Views
46 Views- Read more about Burrows-Wheeler Transform on Purely Morphic Words
- 3 comments
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 78 Views
78 Views
- Read more about x3: Lossless Data Compressor
- Log in to post comments
x3 is a lossless optimizing dictionary-based data compressor. The algorithm uses a combination of a dictionary, context modeling, and arithmetic coding. Optimization adds the ability to find the most appropriate parameters for each file. Even without optimization, x3 can compress data with a compression ratio comparable to the best dictionary compression methods like LZMA, zstd, or Brotli.
slides.pdf
- Categories:
 57 Views
57 Views
- Read more about Contact Matrix Compressor
- 2 comments
- Log in to post comments
The study of three-dimensional folding of chromosomes is important to understand genomics processes. This is done through techniques, such as Hi-C, that analyze the spatial organization of chromosomes in a cell. The data coming from the study is a 2-dimensional quantitative maps with genomic coordinate systems. We present a novel approach called Contact Matrix Compressor(CMC) for the efficient compression of Hi-C data. By exploiting the properties of the data, such as diagonally dominant and symmetrical, CMC achieves a much higher compression.
- Categories:
 43 Views
43 Views
- Read more about On dynamic bitvector implementations
- 2 comments
- Log in to post comments
Bitvectors that support rank and select queries are the workhorses of succinct data structures, implementations of which are now widespread, for example, in bioinformatics software. To date, however, most bitvector implementations are static, thus forcing more complex data structures built from them to be static too. In this paper we explore dynamic bitvectors, which, in addition to rank and select queries, also support update operations, specifically: insert, remove, and modify. We first provide several practical optimizations to the recent B-tree based bitvectors of Prezza (Proc.
- Categories:
 138 Views
138 Views
- Read more about Selective Weighted Adaptive Coding
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views
- Read more about A Huffman Code Based Crypto-System
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 96 Views
96 Views
- Read more about FM-Indexing Grammars Induced by Suffix Sorting for Long Patterns
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 60 Views
60 Views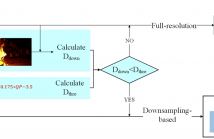
Resampling-based coding, i.e. down-sampling before encoding and up-sampling after decoding, has been recognized to be an effective tool for compressing high-resolution videos at low bitrates. The newest video coding standard, Versatile Video Coding (VVC), supports resampling-based coding via a mechanism named Reference Picture Resampling (RPR), where the spatial resolution can be changed without inserting an intra frame. Intuitively, it is not wise to utilize a single resolution throughout the whole video, because frames with different contents may prefer different coding resolutions.
- Categories:
 270 Views
270 Views