ICASSP is the world's largest and most comprehensive technical conference on signal processing and its applications. It provides a fantastic networking opportunity for like-minded professionals from around the world. ICASSP 2016 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers and cutting-edge session topics.
- Read more about Resource Allocation for Asynchronous Cognitive Radio Networks with FBMC/OFDM under Statistical CSI
- Log in to post comments
This paper studies resource allocation for a multi-carrier based cognitive radio network under the assumption of statistical channel state information (CSI). To circumvent the inherent high computational complexity investigating the joint power-rate-subcarrier of the outage-constrained sum rate maximization problem, we adopt a sub-optimal strategy by solving independently the subcarrier and power-rate problem. Firstly, we propose a heuristic subcarrier allocation paradigm by utilizing an outage-based metric.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views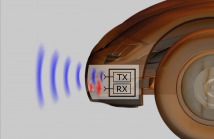
Our demonstrator verifies a novel concept to mitigate unwanted close signal reflections in FMCW radar transceivers. In automotive applications, for instance, these reflections originate from the car’s own bumper, causing a severe degradation of detection sensitivity and accuracy due to the unpreventable phase noise contained in the transmit signal. We propose a concept on how to mitigate the so-called Short-Range (SR) leakage in a recently puplished paper in the IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing (December 2015).
- Categories:
 94 Views
94 ViewsWe consider the problem of quickly detecting an abrupt change of linear coefficients in linear regression models. In particular, the observer sequentially observes a sequence of observations $\{ (x_n; y_n) \}_{n=1}^{\infty}$, which is assumed to obey a linear regression model at each time slot n. Some of the coefficients in the linear model change at a fixed but unknown time $t$. The post-change linear coefficients are unknown to the observer. The observer aims to design an online algorithm to detect the model change based on his sequential observations.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views- Read more about ACCELERATING MULTI-USER LARGE VOCABULARY CONTINUOUS SPEECH RECOGNITION ON HETEROGENEOUS CPU-GPU PLATFORMS
- Log in to post comments
In our previous work, we developed a GPU-accelerated speech recognition engine optimized for faster than real time speech recognition on a heterogeneous CPU-GPU architecture. In this work, we focused on developing a scalable server-client architecture specifically optimized to simultaneously decode multiple users in real-time.
- Categories:
 1 Views
1 Views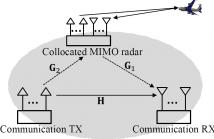
- Read more about A JOINT DESIGN APPROACH FOR SPECTRUM SHARING BETWEEN RADAR AND COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
- Log in to post comments
A joint design approach is proposed for spectrum sharing between MIMO radar and MIMO communication systems. Radar transmit precoding and adaptive communication transmission are adopted, and are jointly designed to maximize signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR) at the radar receiver subject to the communication system meeting certain rate and power constraints. We start with the design of a system in which knowledge of the target information is used. Such design can be used to benchmark the performance of schemes that do not use target information.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views
- Read more about Intrinsic Two-Dimensional Local Structures for Micro-Expression Recognition
- Log in to post comments
An elapsed facial emotion involves changes of facial contour due to the motions (such as contraction or stretch) of facial muscles located at the eyes, nose, lips and etc. Thus, the important information such as corners of facial contours that are located in various regions of the face are crucial to the recognition of facial expressions, and even more apparent for micro-expressions. In this paper, we propose the first known notion of employing intrinsic two-dimensional (i2D) local structures to represent these features for micro-expression recognition.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views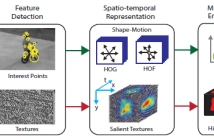
- Read more about Spatio-Temporal Mid-Level Feature Bank for Action Recognition in Low Quality Video
- Log in to post comments
It is a great challenge to perform high level recognition tasks on videos that are poor in quality. In this paper, we propose a new spatio-temporal mid-level (STEM) feature bank for recognizing human actions in low quality videos. The feature bank comprises of a trio of local spatio-temporal features, i.e. shape, motion and textures, which respectively encode structural, dynamic and statistical information in video. These features are encoded into mid-level representations and aggregated to construct STEM.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views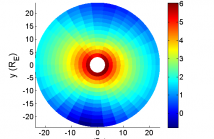
- Read more about Tomographic Reconstruction of Atmosphric Density with Mumford-Shah Functionals
- Log in to post comments
Knowledge of the three-dimensional spatial structure of Earth's uppermost atmosphere is necessary both to understand its role as a dynamic buffer against the solar-driven environment of interplanetary space as well as to assess the rate of its permanent escape from Earth's gravity through evaporation. The only available means of inferring atmospheric structure at these altitudes is through space-based remote sensing of solar radiation that is resonantly scattered or fluoresced by the ambient atoms.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views- Read more about ENERGY DETECTION IN ISI CHANNELS USING LARGE-SCALE RECEIVER ARRAYS_PRESENTATION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views