ICASSP is the world's largest and most comprehensive technical conference on signal processing and its applications. It provides a fantastic networking opportunity for like-minded professionals from around the world. ICASSP 2016 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers and cutting-edge session topics.
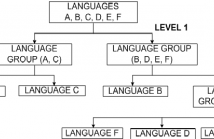
Most current language recognition systems model different levels of information such as acoustic, prosodic, phonotactic, etc. independently and combine the model likelihoods in order to make a decision. However, these are single level systems that treat all languages identically and hence incapable of exploiting any similarities that may exist within groups of languages.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views- Read more about Ship wake detection for sar images with complex backgrounds based on morphological dictionary learning
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views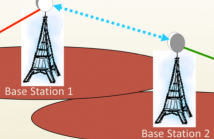
- Read more about STUDY OF ATTENUATION DUE TO WET ANTENNA IN MICROWAVE RADIO COMMUNICATION
- Log in to post comments
Atmospheric conditions are known to affect the Received Sig- nal Level (RSL) in commercial microwave links (MWLs), that operate at frequencies of tens of GHz. Study of these ef- fects is of great importance both for communication engineers and for environmental monitoring. In this paper we study the phenomenon of a wet antenna. During periods of high rela- tive humidity (RH), a thin layer of water may collect on the outside cover of the microwave units, resulting in increased signal attenuation. Here, we focus on the estimation of the signal power loss caused due to this phenomenon.
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views- Read more about USING CONDITIONAL RESTRICTED BOLTZMANN MACHINES FOR SPECTRAL ENVELOPE MODELING IN SPEECH BANDWIDTH EXTENSION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 ViewsThe High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) standard provides a substantial improvement in coding efficiency over previous video coding standards at the cost of a higher computational complexity. HEVC employs a quadtree based image structure by partitioning the image into coding units (CUs). Finding the optimal CU size in terms of rate-distortion is one of the most computationally challenging parts of any HEVC encoder.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views- Read more about FAST AND EFFICIENT REJECTION OF BACKGROUND WAVEFORMS IN INTERICTAL EEG
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views- Read more about EPILEPTIFORM SPIKE TEMPLATE SELECTION USING DYNAMIC TIME WARPING AND AFFINITY PROPAGATION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views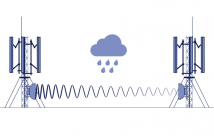
- Read more about CALIBRATION OF THE ATTENUATION-RAIN RATE POWER-LAW PARAMETERS USING MEASUREMENTS FROM COMMERCIAL MICROWAVE NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
In this research we present a new approach for calibration of the Power-Law parameters, using the available commercial microwave links min/max attenuation measurements, and measurements from standard rain-gauges. This calibration process was tested in a real world scenario, and showed promising results.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
- Read more about Joint Instance and Feature Importance Re-weighting for Person Reidentification
- Log in to post comments
Person reidentification refers to the task of recognizing the same person
under different non-overlapping camera views. Presently, person
reidentification based on metric learning is proved to be effective among
various techniques, which exploits the labeled data to learn
a subspace that maximizes the inter-person divergence while minimizes
the intra-person divergence. However, these methods fail to
take the different impacts of various instances and local features into
account. To address this issue, we propose to learn a projection matrix
icassp_zq.pdf
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views