ICASSP is the world's largest and most comprehensive technical conference on signal processing and its applications. It provides a fantastic networking opportunity for like-minded professionals from around the world. ICASSP 2016 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers and cutting-edge session topics.

- Read more about Supervised-learning based face hallucination for enhancing face recognition
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents a two-step supervised face hallucination framework based on class-specific dictionary learning. Since the performance of learning-based face hallucination relies on its training set, an inappropriate training set (e.g., an input face image is very different from the training set) can reduce the visual quality of reconstructed high-resolution (HR) face significantly.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Read more about Distributed Linear Blind Source Separation over Wireless Sensor Networks with Arbitrary Connectivity Patterns
- Log in to post comments
Broad areal coverage and low cost make wireless sensor networks natural platforms for blind source separation (BSS). In this context, distributed processing is attractive because of low power requirements and scalability. However, existing distributed BSS algorithms either require a fully connected pattern of connectivity or require a high computational load at each sensor node. We introduce a distributed robust BSS algorithm that uses a fully shared computation and can be applied over any connected graph.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views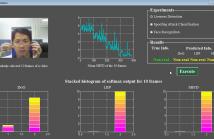
- Read more about Face Liveness Detection Using Shearlet Based Feature Descriptors
- Log in to post comments
We demonstrate the results of DoG and LBP for comparison purpose. This demo video is available at this link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kUCC0hLSJaU. In addition, in order to show that the proposed method can be directly used in real situation, we completed a real-time implementation of our method and tested it using real data which also include print photo attack, mobile photo attack and video attack. In this demo, 21 frames are analyzed for each detection and the final result is the average score of these 21 frames.
- Categories:
 55 Views
55 Views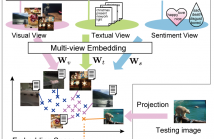
- Read more about IMAGE SENTIMENT ANALYSIS USING LATENT CORRELATIONS AMONG VISUAL, TEXTUAL, AND SENTIMENT VIEWS
- Log in to post comments
As Internet users increasingly post images to express their daily sentiment and emotions, the analysis of sentiments in user-generated images is of increasing importance for developing several applications. Most conventional methods of image sentiment analysis focus on the design of visual features, and the use of text associated to the images has not been sufficiently investigated. This paper proposes a novel approach that exploits latent correlations among multiple views: visual and textual views, and a sentiment view constructed using SentiWordNet.
- Categories:
 57 Views
57 Views- Read more about FACE LIVENESS DETECTION AND RECOGNITION USING SHEARLET BASED FEATURE DESCRIPTORS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views- Read more about A novel array processing method for precise depth detection of ultrasound point scatter
- Log in to post comments
A signal based algorithm resulting in increased depth resolution is presented for medical ultrasound. It relies on multiple foci beamforming that is enabled by current ultrasound imaging systems. The concept stems from optical microscopy and is translated here into ultrasound using the Field II simulation software. A 7 MHz linear transducer is used to scan a single point scatterer phantom that can move in the axial direction.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views- Read more about Super-resolution spectral analysis for ultrasound scatter characterization
- Log in to post comments
Parametric Bayesian spectral estimation methods have been previously utilized to improve frequency resolution. Ultrasound signals have been tested in such methods resulting in higher precision frequency detection compared to common non-parametric spectral estimation methods based on the Fourier transform. Such a technique using a reversible jump Markov Chain Monte Carlo algorithm has been developed to fully characterize signals and in addition to frequency, to provide amplitude and noise estimation.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views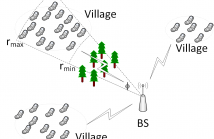
- Read more about Directional Maximum Likelihood Self-Estimation of the Path-Loss Exponent
- Log in to post comments
The path-loss exponent (PLE) is a key parameter in wireless propagation channels. Therefore, obtaining the knowledge of the PLE is rather significant for assisting wireless communications and networking to achieve a better performance. Most existing methods for estimating the PLE not only require nodes with known locations but also assume an omni-directional PLE. However, the location information might be unavailable or unreliable and, in practice, the PLE might change with the direction.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views- Read more about 1-Bit Compressed Sensing Of Positive Semi-Definite Matrices Via Rank-1 Measurement Matrices
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we investigate the problem of recovering positive semi-definite (PSD) matrix from 1-bit sensing. The measurement matrix is rank-1 and constructed by the outer product of a pair of vectors, whose entries are independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.) Gaussian variables. The recovery problem is solved in closed form through a convex programming. Our analysis reveals that the solution is biased in general. However, in case of error-free measurement, we find that for rank-r PSD matrix with bounded condition number, the bias decreases with an order of O(1/r).
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views