
ICASSP is the world's largest and most comprehensive technical conference on signal processing and its applications. It provides a fantastic networking opportunity for like-minded professionals from around the world. ICASSP 2017 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers and cutting-edge session topics. Visit ICASSP 2017
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views- Read more about Effect of Acoustic Conditions on Algorithms to Detect Parkinson’s Disease from Speech
- Log in to post comments
Automatic detection of Parkinson's disease (PD) from speech is a basic step towards computer-aided tools supporting the diagnosis and monitoring of the disease. Although several methods have been proposed, their applicability to real-world situations is still unclear. In particular, the effect of acoustic conditions is not well understood. In this paper, the effects on the accuracy of five different methods to detect PD from speech are evaluated.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views- Read more about LINE DETECTION IN SPECKLE IMAGES USING RADON TRANSFORM AND L1 REGULARIZATION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views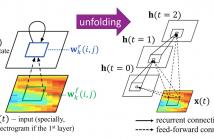
- Read more about RECURRENT CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORK FOR SPEECH PROCESSING
- Log in to post comments
Different neural networks have exhibited excellent performance on various speech processing tasks, and they usually have specific advantages and disadvantages. We propose to use a recently developed deep learning model, recurrent convolutional neural network (RCNN), for speech processing, which inherits some merits of recurrent neural network (RNN) and convolutional neural network (CNN). The core module can be viewed as a convolutional layer embedded with an RNN, which enables the model to capture both temporal and frequency dependence in the spectrogram of the speech in an efficient way.
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views- Read more about Dynamic Probabilistic Linear Discriminant Analysis for Face Recognition in Videos
- Log in to post comments
Component Analysis (CA) for computer vision and machine learning comprises of a set of statistical techniques that decompose visual data to appropriate latent components that are relevant to the task-at-hand, such as alignment, clustering, segmentation, classification etc. The past few years we have witnessed an explosion of research in component analysis, introducing both novel deterministic and probabilistic models (e.g., Probabilistic Principal Component Analysis (PPCA), Probabilistic Linear Discriminant Analysis (PLDA), Probabilistic Canonical Correlation Analysis (PCCA) etc.).
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views- Read more about Face Recognition in real-world images
- Log in to post comments
Face recognition systems are designed to handle well-aligned images captured under controlled situations. However real-world images present varying orientations, expressions, and illumination conditions. Traditional face recognition algorithms perform poorly on such images. In this paper we present a method for face recognition adapted to real-world conditions that can be trained using very few training examples and is computationally efficient. Our method consists of performing a novel alignment process followed by classification using sparse representation techniques.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views- Read more about SPEAKER DIARIZATION: A PERSPECTIVE ON CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES FROM THEORY TO PRACTICE
- Log in to post comments
This paper discusses some challenges and opportunities in developing a speaker diarization system for operation on real world call center telephony data. We contrast some of the differences between a standard data set akin to NIST evaluations and those found in call centers. In exploring these differences we discovered vulnerabilities and proposed changes to address them.
 15 Views
15 Views- Read more about Learning Cross-lingual Knowledge with Multilingual BLSTM for Emphasis Detection with Limited Training Data
- Log in to post comments
Bidirectional long short-term memory (BLSTM) recurrent neural network (RNN) has achieved state-of-the-art performance in many sequence processing problems given its capability in capturing contextual information. However, for languages with limited amount of training data, it is still difficult to obtain a high quality BLSTM model for emphasis detection, the aim of which is to recognize the emphasized speech segments from natural speech.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 ViewsBiomedical images are usually corrupted by strong noise and
intensity inhomogeneity simultaneously. Existing regionbased active contour models (RACMs) easily fail when segmenting such images. In the frequency domain, we propose a
generalized RACM that presents a new way to understand the
essence of classical RACMs whose segmentation results are
determined by a frequency filter to extract the proposed frequency boundary energy. Then, we introduce the difference
of Gaussians as the optimal filter to exclude strong noise and
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views