
ICASSP is the world's largest and most comprehensive technical conference on signal processing and its applications. It provides a fantastic networking opportunity for like-minded professionals from around the world. ICASSP 2017 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers and cutting-edge session topics. Visit ICASSP 2017
- Read more about Automatic Radar Waveform Recognition Based on Time-Frequency Analysis and Convolutional Neural Network
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 45 Views
45 Views- Read more about An Online Feature Selection Architecture For Human Activity Recognition
- Log in to post comments
Human Activity Recognition (HAR) must currently face up to the challenge of rethinking analytics from the perspective of real-time operation, wherein biophysical sensing streams are efficiently intertwined at close vicinity to the point of sensing. As such, feature selection techniques, traditionally employed for off-line data processing, should be evaluated with respect to their ability to filter out redundant information in real-time.
- Categories:
 2 Views
2 Views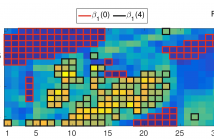
- Read more about Constrain the Docile CTUs: an In-Frame Complexity Allocator for HEVC Intra Encoders
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views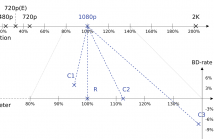
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views- Read more about Affect Recognition from Lip Articulations
- Log in to post comments
Lips deliver visually active clues for speech articulation. Affective states define how humans articulate speech; hence, they also change articulation of lip motion. In this paper, we investigate effect of phonetic classes for affect recognition from lip articulations. The affect recognition problem is formalized in discrete activation, valence and dominance attributes. We use the symmetric Kullback-Leibler divergence (KLD) to rate phonetic classes with larger discrimination across different affective states. We perform experimental evaluations using the IEMOCAP database.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views- Read more about Use of Affect Based Interaction Classification for Continuous Emotion Tracking
- Log in to post comments
Natural and affective handshakes of two participants define the course of dyadic interaction. Affective states of the participants are expected to be correlated with the nature of the dyadic interaction. In this paper, we extract two classes of the dyadic interaction based on temporal clustering of affective states. We use the k-means temporal clustering to define the interaction classes, and utilize support vector machine based classifier to estimate the interaction class types from multimodal, speech and motion, features.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views- Read more about Massive MIMO Processing at the Semiconductor Edge: Exploring the System and Circuit Margins for Power Saving
- Log in to post comments
In this work, we consider the potential of processing at the semiconductor edge by allowing voltage over-scaling and complete antenna signal failures, focusing on the per-antenna digital functionality that dominant the DSP complexity. The impact of the resulting hardware errors on the performance of Massive MIMO transmission is analyzed. It shows that the inherent redundancy in the system brings a solid tolerance to sporadic hardware errors. Potential control tactics are introduced, that could further optimize the operation of the error-prone circuitry.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 ViewsRadar waveforms often need to be optimized to achieve minimal sidelobes in the ambiguity function. In this paper, it is shown that sampling rate can affect the optimality of the sidelobe level, so the sampling rate should be considered already at the optimization phase. A theorem for the cross-ambiguity function peak values of the oversampled waveforms is developed.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views- Read more about Reduction of Necessary Data Rate for Neural Data Through Exponential and Sinusoidal Spline Decomposition using the Finite Rate of Innovation Framework
- Log in to post comments
The sampling of neural signals plays an important role in modern neuroscience, especially for prosthetics. However, due to hardware and data rate constraints, only spike trains can get recovered reliably. State of the art prosthetics can still achieve impressive results, but to get higher resolutions the used data rate needs to be reduced. In this paper, this is done by expressing the data with exponential and sinusoidal splines.
FRIVortrag.pdf
FRIVortrag.pdf
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views- Read more about NON-SEPARABLE QUADRUPLE LIFTING STRUCTURE FOR FOUR-DIMENSIONAL INTEGER WAVELET TRANSFORM WITH REDUCED ROUNDING NOISE
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
The Wavelet Transform (WT) in JPEG 2000 is using a ‘separable’ lifting structure, where the one-dimensional (1D) transform is put into multidimensional image signal of its spatial and temporal dimensions. A ‘non-separable’ three-dimensional (3D) structure as the existing method is used to minimize its lifting steps. The ‘non-separable’ 3D structure in the (5,3) type transform for lossless coding is proved to reduce the rounding noise inside it. However, in the (9,7) type transform for lossy coding, the rounding noise inside the ‘non-separable’ 3D structure has increased.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views