
ICASSP is the world's largest and most comprehensive technical conference on signal processing and its applications. It provides a fantastic networking opportunity for like-minded professionals from around the world. ICASSP 2017 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers and cutting-edge session topics. Visit ICASSP 2017
- Read more about Constrained Perturbation Regularization Approach for Signal Estimation Using Random Matrix Theory
- Log in to post comments
In this work, we propose a new regularization approach for linear least-squares problems with random matrices. In
the proposed constrained perturbation regularization approach, an artificial perturbation matrix with a bounded norm is forced
into the system model matrix. This perturbation is introduced to improve the singular-value structure of the model matrix and,
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views- Read more about A SEMI-SUPERVISED METHOD FOR MULTI-SUBJECT FMRI FUNCTIONAL ALIGNMENT
- Log in to post comments
Practical limitations on the duration of individual fMRI scans have led neuroscientist to consider the aggregation of data from multiple subjects. Differences in anatomical structures and functional topographies of brains require aligning data across subjects. Existing functional alignment methods serve as a preprocessing step that allows subsequent statistical methods to learn from the aggregated multi-subject data. Despite their success, current alignment methods do not leverage the labeled data used in the subsequent methods.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views- Read more about Demixing Sparse Signals via Convex Optimization
- Log in to post comments
We consider demixing a pair of sparse signals in orthonormal basis via convex optimization. Theoretically, we characterize the condition under which the solution of the convex optimization problem correctly demixes the true signal components. In specific, we introduce the local subspace coherence to characterize how a basis vector is coherent with a signal subspace, and show that the convex optimization approach succeeds if the subspaces of the true signal components avoid high local subspace coherence.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views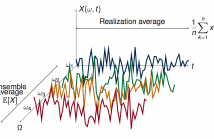
The ability to obtain accurate estimators from a set of measurements is a key factor in science and engineering. Typically, there is an inherent assumption that the measurements were taken in a sequential order, be it in space or time. However, data is increasingly irregular so this assumption of sequentially obtained measurements no longer holds. By leveraging notions of graph signal processing to account for these irregular domains, we propose an unbiased estimator for the mean of a wide sense stationary graph process based on the diffusion of a single realization.
- Categories:
 99 Views
99 Views- Read more about SPEECH DEREVERBERATION USING NMF WITH REGULARIZED ROOM IMPULSE RESPONSE
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, various regularizations on the room impulse response
(RIR) are proposed to obtain better single-channel speech derever-
beration in the non-negative matrix factorization (NMF) framework.
The regularizations on the RIR are motivated by the spectral domain
representation of the RIR. To obtain better estimates of the RIR and
clean speech, we propose three modifications (i) to obtain a sparse
RIR (ii) a frequency envelop constrained RIR and (iii) to include the
early part of the RIR. The performance of the proposed regularizers
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views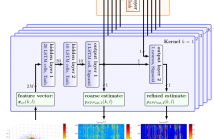
- Read more about DNN-based Speech Mask Estimation for Eigenvector Beamforming
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views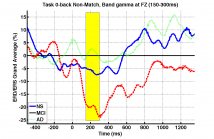
- Read more about EVENT-RELATED SYNCHRONISATION RESPONSES TO N-BACK MEMORY TASKS DISCRIMINATE BETWEEN HEALTHY AGEING, MILD COGNITIVE IMPAIRMENT, AND MILD ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE
- Log in to post comments
In this study we investigate whether or not event-related (de)synchronisation (ERD/ERS) can be used to differenti- ate between 27 healthy elderly, 21 subjects diagnosed with amnestic mild cognitive impairment (aMCI) and 16 mild Alzheimer’s disease (AD) patients. Using 32-channel EEG recordings, we measured ERD responses to a three-level vi- sual N-back task (N = 0, 1, 2) on the well-known delta, theta, alpha, beta and gamma bands.
- Categories:
 46 Views
46 Views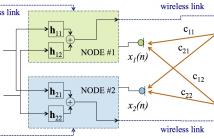
- Read more about Channel estimation for crosstalk cancellation in wireless acoustic networks
- Log in to post comments
In this paper we deal with the estimation of the room impulse response (RIR) between each loudspeaker and each microphone of a wireless acoustic network of two nodes when used to implement a crosstalk canceller. The nodes of the network are commercial devices connected via standard wireless links, presenting low computational requirements and non-ideal synchronization between them. Moreover, the nodes can exchange information, but they cannot share their signals due to the high throughput and perfect synchronism that would be required.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views- Read more about Energy Blowup for Truncated Stable LTI Systems
- Log in to post comments
In this paper we analyze the convergence behavior of a sampling based system approximation process, where the time variable is in the argument of the signal and not in the argument of the bandlimited impulse response. We consider the Paley-Wiener space $PW_\pi^2$ of bandlimited signals with finite energy and stable linear time-invariant (LTI) systems, and show that there are signals and systems such that the approximation process diverges in the $L^2$-norm, i.e., the norm of the signal space. We prove that the sets of signals and systems creating divergence are jointly spaceable, i.e., there exists an infinite dimensional closed subspace of $PW_\pi^2$ and an infinite dimensional closed subspace of the space of all stable LTI systems, such that the approximation process diverges for any non-zero pair of signal and system from these subspaces.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views