
ICASSP is the world's largest and most comprehensive technical conference on signal processing and its applications. It provides a fantastic networking opportunity for like-minded professionals from around the world. ICASSP 2017 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers and cutting-edge session topics. Visit ICASSP 2017
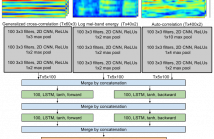
- Read more about Sound Event Detection Using Spatial Features and Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 60 Views
60 Views- Read more about Automatic segmentation of retinal vasculature
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 ViewsThis paper proposes a novel inverse TMO, which enables to generate
HDR images from LDR ones,
not only without using any specific parameters but also at low
computing costs.
Furthermore, the inverse TMO has a new characteristic when an
LDR image is mapped from an HDR one by Reinhard's global operator.
In the case, the HDR image reconstructed by the proposed method
without parameters can be remapped into the same image as
that remapped from an HDR one reconstructed with parameters.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views- Read more about RECURSIVE LEAST-SQUARES ALGORITHMS FOR SPARSE SYSTEM MODELING
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose some sparsity aware algorithms, namely the Recursive least-Squares for sparse systems (S-RLS) and l0-norm Recursive least-Squares (l0-RLS), in order to exploit the sparsity of an unknown system. The first algorithm, applies a discard function on the weight vector to disregard the coefficients close to zero during the update process. The second algorithm, employs the sparsity-promoting scheme via some non-convex approximations to the l0-norm.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views- Read more about ICASSP2017 Poster (Paper #4319)
- Log in to post comments
The performance of automatic speech recognition (ASR) system is often degraded in adverse real-world environments. In recent times, deep learning has successfully emerged as a breakthrough for acoustic modeling in ASR; accordingly, deep-neural-network(DNN)-based speech feature enhancement (FE) approaches have attracted much attention owing to their powerful modeling capabilities. However, DNN-based approaches are unable to achieve remarkable performance improvements for speech with severe distortion in the test environments different from training environments.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 ViewsDeep learning has significantly advanced state-of-the-art of speech
recognition in the past few years. However, compared to conventional
Gaussian mixture acoustic models, neural network models are
usually much larger, and are therefore not very deployable in embedded
devices. Previously, we investigated a compact highway deep
neural network (HDNN) for acoustic modelling, which is a type
of depth-gated feedforward neural network. We have shown that
HDNN-based acoustic models can achieve comparable recognition
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views- Read more about Joint Optimisation of Tandem Systems using Gaussian Mixture Density Neural Network Discriminative Sequence Training
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views- Read more about Semantic Mapping of Natural Language Input to Database Entries via Convolutional Neural Networks
- Log in to post comments
Natural language processing research has made major advances with the concept of representing words, sentences, paragraphs, and even documents by embedded vector representations. We apply this idea to the problem of relating foods, as expressed in natural language meal descriptions, to corresponding database entries. We generate fixed-length embeddings for U.S.
icassp_17.pdf
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about MULTI-SCALE SPOT SEGMENTATION WITH SELECTION OF IMAGE SCALES
- Log in to post comments
Detecting spot-like objects of different sizes in images is needed in many applications. Multiple image scales must then be handled for reliable spot segmentation.
We define an original criterion based on the a contrario approach and the LoG scale-space framework to automatically select the meaningful scales.
We then design a coarse-to-fine multi-scale spot segmentation scheme involving
a locally adaptive thresholding across scales, to come up with the final map of segmented spots.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views