
ICASSP is the world's largest and most comprehensive technical conference on signal processing and its applications. It provides a fantastic networking opportunity for like-minded professionals from around the world. ICASSP 2017 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers and cutting-edge session topics. Visit ICASSP 2017
- Read more about Detection of urban trees in multiple-source aerial data (optical, infrared, DSM)
- Log in to post comments
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 76 Views
76 Views
- Read more about PARAMETER ESTIMATION FROM HETEROGENEOUS/MULTIMODAL DATA SETS
- Log in to post comments
Optimal parameter estimation requires simultaneous processing of all available measurements.
The complexity of this task may become too large when measurements from two or more multimodal sensor networks are avaliable.
In such cases, fusion of estimates obtained from each data set separately may be practical.
In this paper, we derive the optimal linear combination of the possibly non-linear estimators, and propose sub-optimal weightings.
We analyze the asymptotic performance gain of the first suboptimal approach with respect to the individual optimal estimates.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views- Read more about A KNOWLEDGE TRANSFER AND BOOSTING APPROACH TO THE PREDICTION OF AFFECT IN MOVIES
- Log in to post comments
Affect prediction is a classical problem and has recently garnered special interest in multimedia applications. Affect prediction in movies is one such domain, potentially aiding the design as well as the impact analysis of movies.Given the large diversity in movies (such as different genres and languages), obtaining a comprehensive movie dataset for modeling affect is challenging while models trained on smaller datasets may not generalize. In this paper, we address the problem of continuous affect ratings with the availability of limited in-domain data resources.
SigPort.zip
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views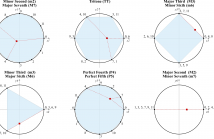
In this paper we present the INESC Key Detection (IKD) system which incorporates a novel method for dynamically biasing key mode estimation using the spatial displacement of beat-synchronous Tonal Interval Vectors (TIVs). We evaluate the performance of the IKD system at finding the global key on three annotated audio datasets and using three key-defining profiles.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views- Read more about LEARNING TIME VARYING GRAPHS
- Log in to post comments
We consider the problem of inferring the hidden structure of high-dimensional
time-varying data. In particular, we aim at capturing
the dynamic relationships by representing data as valued nodes in a
sequence of graphs. Our approach is motivated by the observation
that imposing a meaningful graph topology can help solving the generally
ill-posed and challenging problem of structure inference. To
capture the temporal evolution in the sequence of graphs, we introduce
a new prior that asserts that the graph edges change smoothly
- Categories:
 63 Views
63 Views- Read more about : Faster-than-Nyquist Spatiotemporal Symbol-level Precoding in the Downlink of Multiuser MISO Channels
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views- Read more about A FULL REFERENCE STEREOSCOPIC VIDEO QUALITY ASSESSMENT METRIC
- Log in to post comments
We propose a full reference stereo video quality assessment
algorithm for assessing the perceptual quality of natural stereo
videos. We exploit the separable representation of motion
and binocular disparity in the visual cortex and develop a
four stage algorithm to measure the quality of a stereoscopic
video called FLOSIM3D. First, we compute the temporal features
by utilizing an existing 2D VQA metric which measures
the temporal annoyance based on patch level statistics such
as mean, variance and minimum eigen value and pools them
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about Summarization of Human Activity Videos Via Low-Rank Approximation
- Log in to post comments
Summarization of videos depicting human activities is a timely problem with important applications, e.g., in the domains of surveillance or film/TV production, that steadily becomes more relevant. Research on video summarization has mainly relied on global clustering or local (frame-by-frame) saliency methods to provide automated algorithmic
- Categories:
 2 Views
2 Views
- Read more about Summarization of Human Activity Videos Via Low-Rank Approximation
- Log in to post comments
Summarization of videos depicting human activities is a timely problem with important applications, e.g., in the domains of surveillance or film/TV production, that steadily becomes more relevant. Research on video summarization has mainly relied on global clustering or local (frame-by-frame) saliency methods to provide automated algorithmic
- Categories:
 2 Views
2 Views
- Read more about Summarization of Human Activity Videos Via Low-Rank Approximation
- Log in to post comments
Summarization of videos depicting human activities is a timely problem with important applications, e.g., in the domains of surveillance or film/TV production, that steadily becomes more relevant. Research on video summarization has mainly relied on global clustering or local (frame-by-frame) saliency methods to provide automated algorithmic
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views