
ICASSP is the world's largest and most comprehensive technical conference on signal processing and its applications. It provides a fantastic networking opportunity for like-minded professionals from around the world. ICASSP 2017 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers and cutting-edge session topics. Visit ICASSP 2017
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views- Read more about Efficient Single/Multiple Unimodular Waveform Design With Low Weighted Correlatioins
- Log in to post comments
A new method for designing single/multiple unimodular waveforms with good weighted correlation properties, which is
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views- Read more about TWO-STAGE FACIAL AGE PREDICTION USING GROUP-SPECIFIC FEATURES
- Log in to post comments
A novel two-stage age prediction approach with group-specific features is proposed in this paper. Aging process is captured through a highly discriminating feature representation that models shape, appearance, skin spots, and wrinkles. The two-stage method consists of a multi-class Support Vector Machine (SVM) to predict the age bracket while the final age prediction is carried out using Support Vector Regression (SVR). The novelty of our work is that the feature extraction is group-specific and can therefore be tailored to each age bracket in the specific age prediction step.
ICASSP2017.pdf
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views- Read more about Through-the-Wall Radar Signal Classification using Discriminative Dictionary Learning
- Log in to post comments
Through-the-wall radar imaging is an electromagnetic wave sensing technology capable of detecting targets behind walls, doors, and opaque obstacles. Identification of stationary targets is often achieved by first forming an image of the scene, and then segmenting and classifying the targets of interest. In order to provide prompt and reliable situational awareness, this paper proposes a radar signal classification approach that does not rely on image formation.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views- Read more about Online Learning of Time-Frequency Patterns
- Log in to post comments
We present an online method to learn recurring time-frequency patterns from spectrograms. Our method relies on a convolutive decomposition that estimates sequences of spectra into time-frequency patterns and their corresponding activation signals. This method processes one spectrogram at a time such that in comparison with a batch method, the computational cost is reduced proportionally to the number of considered spectrograms. We use a first-order stochastic gradient descent and show that a monotonically decreasing learning-rate works appropriately.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about UNIQUE: Unsupervised Image Quality Estimation
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we estimate perceived image quality using sparse representations obtained from generic image databases through an unsupervised learning approach. A color space transformation, a mean subtraction, and a whitening operation are used to enhance descriptiveness of images by reducing spatial redundancy; a linear decoder is used to obtain sparse representations; and a thresholding stage is used to formulate suppression mechanisms in a visual system.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views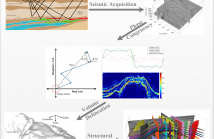
- Read more about Phase Congruency for Image Understanding with Applications in Computational Seismic Interpretation
- Log in to post comments
Phase Congruency (PC) can highlight small discontinuities in images with varying illumination and contrast using the congruency of phase in Fourier components. PC can not only detect the subtle variations in the image intensity but can also highlight the anomalous values to develop a deeper understanding of the images content and context. In this paper, we propose a new method based on PC for computational seismic interpretation with an application to subsurface structures delineation within migrated seismic volumes.
ICASSP_20170214.pdf
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views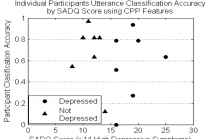
- Read more about DETECTING STRESS AND DEPRESSION IN ADULTS WITH APHASIA THROUGH SPEECH ANALYSIS
- Log in to post comments
Aphasia is an acquired communication disorder resulting from brain damage and impairs an individual’s ability to use, produce, and comprehend language. Loss of communication skills can be stressful and may result in depression, yet most stress and depression diagnostic tools are designed for adults without aphasia. This project is a research effort to predict stress and depression from acoustic profiles of adults with aphasia using linear support-vector regression. The labels were obtained through caregiver surveys (SADQ-10) or surveys not designed for adults with aphasia (PSS).
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views- Read more about OBJECT DETECTION REFINEMENT USING MARKOV RANDOM FIELD BASED PRUNING AND LEARNING BASED RESCORING
- Log in to post comments
Contextual information such as the co-occurrence of objects and the location of objects has played an important role in object detec- tion. We present candidate pruning and object rescoring methods that leverage contextual information and that can improve the state- of-the-art CNN-based object detection methods such as Fast R-CNN and Faster R-CNN. In our pruning method, we formulate candidate reduction as a Markov random field optimization problem. In our rescoring method, we employ a machine learning technique to recon- sider the detection scores of candidate windows.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views